机器学习 -- 人工智能学习路线(进行中……)
深度学习与炼丹。 经典网络 AlexNet 第一层的卷积内核是 11x11 像素。 为什么是 11 不是 10,不是 12?不知道,作者写论文的时候也没讲。 为什么有 9 层,为什么第二层就变成 5x5,后面又变成 3x3 了?作者也没说。 甚至,为什么这个内核的大小越来越小也没有交代。 深度学习像一剂成分复杂、原理不明的药。 卷积架构 适合图像处理,RNN & Transformer 架构适合处理语言。 实践中,根据经验多试几个,哪个网络效果更好就用那个。
机器学习的学习路径
使用 Kaggle 的目的主要是将技能落在实处,防止练就一身屠龙之技。 机器学习最大的幻觉就是觉得自己什么都懂了,但等到真的使用时发现并不奏效,而 Kaggle 是一个低成本的应用机器学习的机会。
工业界百分之六十的时间都在清理数据,这和学术界干净且规则化的现成数据完全不同。
一定要学习优质资源,而不是不分青红皂白的学习。
获取数据的方式主要有三种:开放数据(以学术界开放为主,如 ImageNet 和 LFW)、第三方数据公司的付费数据和结合自身业务产生的数据。
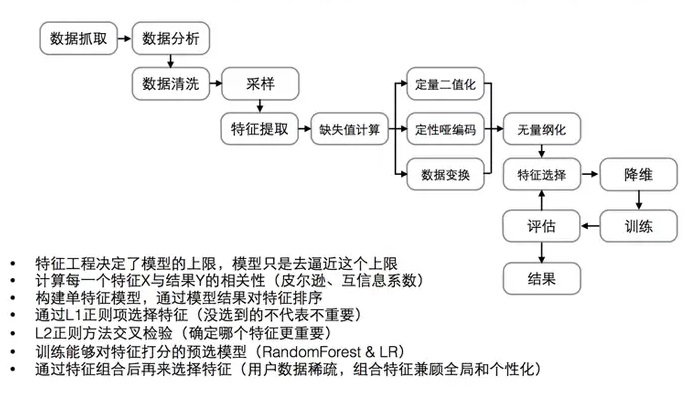
特征工程
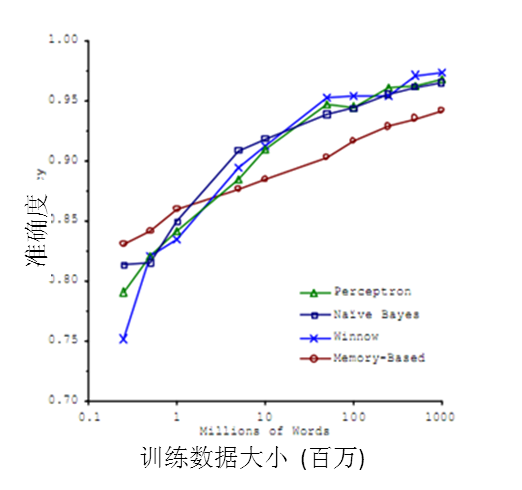
It's not who has the best algorithm that wins. It's who has the most data.
学习地图
- 图片处理 imgaug
- 望舒同学
note
- 一些资料 notes
- 浙江大学 - 机器学习
微积分:MIT 18.01, MIT 18.02 线性代数:MIT 18.06 概率论与数理统计:MIT 6.041 凸优化:CVX101
wechatdl.md rdevblog.md 吴恩达 李沐 李宏毅 李航 李飞飞
后续建议学习李航老师的《统计学习方法》,或者周志华老师的《机器学习》(西瓜书)。
参考书: (1)机器学习, 周志华,清华大学出版社,2016 (2)统计学习方法,李航,清华大学出版社,2012 (3)Machine Learning in Action, P. Harrington, 人民邮电出版社 (4)Deep Learning, I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio and A. Courville, 2016. (5)Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ( 模式识别与机器学习 ),Christopher M. Bishop, 2006 (6)Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective, K. P. Murphy (7)Machine Learning ( 机器学习 ), Tom M. Mitchell, 机械工业出版社,2003 年。
网课: (1) Stanford Web course “Machine Learning” by Andrew Ng https://www.coursera.org/course/ml (2) Stanford Web course (CS231N) by Fei-fei Li https://cs231n.Stanford.edu (3) UCL reinforcement learning course https://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.silver/web/Teaching.html (4) 2017 年课程实录 https://b23.tv/eLlyiPI
本专栏图片、公式很多来自***大学李弘毅老师、斯坦福大学 cs229,斯坦福大学 cs231n 、斯坦福大学 cs224n 课程。在这里,感谢这些经典课程,向他们致敬!
建议可以从吴恩达 / 李宏毅的课程入门,看完后可进一步的根据自己的研究方向选择,比如 CV 方向的可以看李飞飞的 CS231n 课程,最后再直接上手 Pytorch 去学习官方示例,把代码跑起来。
- https://github.com/fengdu78/Coursera-ML-AndrewNg-Notes
- http://www.ai-start.com/ml2014/
- https://scruel.github.io/Notes-ML-AndrewNg/
深度学习与计算机视觉—斯坦福 CS231n https://liumin.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125546056 通道洗牌、变形卷积核、可分离卷积?盘点卷积神经网络中十大令人拍案叫绝的操作。 https://www.jianshu.com/p/71804c97123d
胡浩基?李航 . 统计学习方法 ?,周志华 . 机器学习 ?
- 《统计学习方法》李航?
- 《机器学习课》邹博?周志华?西瓜书?
- 深度学习 计算机视觉 CV、Paper 阅读等等 …
学习计划:
- 从新视频,查漏补缺。
- 查看 week 文档。
- 做作业。
- 最后 2022 版本全部从新过一遍。
第一周的完成了。该第二周了。 第二周 3.1 - 5.7 第三周 6.1 - 7.4 第四周 8.1 - 8.7 第五周 9.1 - 9.8 第六周 10.0 - 11.5 第七周 12.1 - 12.6 第八周 13.1 - 14.7 第九周 15.1 - 16.6 第十周 17.1 - 19.1
朱明瑞
一个别人写的科研经验总结:https://github.com/pengsida/learning_research。
科研基础
- 基础课程:重点掌握《高等数学》《线性代数》《概率论与数理统计》《矩阵论》《凸优化》课程,这里的掌握是要理解它们的本质、作用及物理几何意义,而非应付考试。建议搜索国内外优秀书籍、公开课、视频进行学习。例如,《线性代数》推荐《线性代数的本质》系列视频 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ys411472E,以及 Gilbert Strang 的麻省理工大学公开课视频 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1zx411g7gq。
快速了解机器学习所需要的数学知识,建议学习《Mathematics for Machine Learning》一书。
-
机器学习:推荐国立台湾大学李宏毅机器学习课程 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wv411h7kN?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click,清华大学大佬白板推导系列 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1aE411o7qd?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click。
-
深度学习:推荐 Google 研究科学家 Ian Goodfellow(Generative Adversarial Nets 提出者)的花书《Deep Learning》(有中文译本 人民邮电出版社),斯坦福大学李飞飞(ImageNet 的提出者)老师的 cs231n 计算机视觉课程 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nJ411z7fe。
Jakub Tomczak《深度生成建模》讲座报告与视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1pb4y1s7hS/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=cd39e17f789bd6d503b915533f2c2237
电子书 Deep Generative Modeling:https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-030-93158-2
这些深度生成模型中,重点掌握:
GAN(Generative Adversarial Networks,生成对抗网络)
-
学习 GAN 的原理,可以看 CS231n、李宏毅机器学习相关视频,或者搜一些博客等。
-
跑通 DCGAN 的代码,https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html
-
读 pix2pix 跟 CycleGAN 这两篇论文,弄清楚原理
-
跑通 pix2pix 跟 CycleGAN 代码,https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
-
学习 StyleGAN 与 GAN Inversion、GAN Prior 技术原理
Review
- code\Programming Exercise(代码作业).pdf
- code\ex2-logistic regression\ex2.pdf
- code\ex2-logistic regression\ex2data1.txt
- code\ex2-logistic regression\ex2data2.txt
- code\ex2-logistic regression\ML-Exercise2.ipynb
- code\ex3-neural network\ex3.pdf
- code\ex3-neural network\ex3data1.mat
- code\ex3-neural network\ex3weights.mat
- code\ex3-neural network\ML-Exercise3.ipynb
- code\ex3-neural network\ 向量化标签 .png
- code\ex4-NN back propagation\ex4.pdf
- code\ex4-NN back propagation\ex4data1.mat
- code\ex4-NN back propagation\ex4weights.mat
- code\ex4-NN back propagation\ML-Exercise4.ipynb
- code\ex5-bias vs variance\ex5.pdf
- code\ex5-bias vs variance\ex5data1.mat
- code\ex5-bias vs variance\ML-Exercise5.ipynb
- code\ex6-SVM\ex6.pdf
- code\ex6-SVM\ML-Exercise6.ipynb
- code\ex6-SVM\data\emailSample1.txt
- code\ex6-SVM\data\emailSample2.txt
- code\ex6-SVM\data\ex6data1.mat
- code\ex6-SVM\data\ex6data2.mat
- code\ex6-SVM\data\ex6data3.mat
- code\ex6-SVM\data\spamSample1.txt
- code\ex6-SVM\data\spamSample2.txt
- code\ex6-SVM\data\spamTest.mat
- code\ex6-SVM\data\spamTrain.mat
- code\ex6-SVM\data\vocab.txt
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\ex7.pdf
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\ML-Exercise7.ipynb
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\data\bird_small.mat
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\data\bird_small.png
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\data\ex7data1.mat
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\data\ex7data2.mat
- code\ex7-kmeans and PCA\data\ex7faces.mat
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\ex8.pdf
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\ML-Exercise8.ipynb
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\data\ex8_movieParams.mat
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\data\ex8_movies.mat
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\data\ex8data1.mat
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\data\ex8data2.mat
- code\ex8-anomaly detection and recommendation\data\movie_ids.txt
- docx\README.md
- docx\ 机器学习的数学基础.docx
- markdown\1.CS229-LinearAlgebra.md
- markdown\2.CS229-Prob.md
- markdown\math.md
- markdown\README.md
- markdown\SUMMARY.md
- markdown\week1.md
- markdown\week10.md
- markdown\week2.md
- markdown\week3.md
- markdown\week4.md
- markdown\week5.md
- markdown\week6.md
- markdown\week7.md
- markdown\week8.md
- markdown\week9.md
- ppt\Lecture1.pptx
- ppt\Lecture10.pptx
- ppt\Lecture11.pptx
- ppt\Lecture12.pptx
- ppt\Lecture13.pptx
- ppt\Lecture14.pptx
- ppt\Lecture15.pptx
- ppt\Lecture16.pptx
- ppt\Lecture17.pptx
- ppt\Lecture18.pptx
- ppt\Lecture2.pptx
- ppt\Lecture3.pptx
- ppt\Lecture4.pptx
- ppt\Lecture5.pptx
- ppt\Lecture6.pptx
- ppt\Lecture7.pptx
- ppt\Lecture8.pptx
- ppt\Lecture9.pptx
英语
作业 exercise
Python 实现。
第一周
首先,我们将创建一个以参数 θ 为特征函数的代价函数 \(J\left( \theta \right)=\frac{1}{2m}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{ { {\left( { {h}_{\theta }}\left( { {x}^{(i)}} \right)-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)}^{2}}}\)
其中: \({ {h}_{\theta }}\left( x \right)={ {\theta }^{T}}X={ {\theta }_{0}}{ {x}_{0}}+{ {\theta }_{1}}{ {x}_{1}}+{ {\theta }_{2}}{ {x}_{2}}+...+{ {\theta }_{n}}{ {x}_{n}}\)
# 计算代价函数函数。
def computeCost(X, y, theta):
inner = np.power(((X * theta.T) - y), 2)
return np.sum(inner) / (2 * len(X))
# 批量梯度下降
# alpha -- 学习速率
# iters -- 要执行的迭代次数
def gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha = 0.01, iters = 1000):
temp = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape)) # 跟 theta 一样的矩阵
parameters = int(theta.ravel().shape[1]) # theta 个数,ravel() 将数组维度拉成一维数组
cost = np.zeros(iters) # 初始化 cost 数组。
for i in range(iters):
error = (X * theta.T) - y
for j in range(parameters):
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,j])
temp[0,j] = theta[0,j] - ((alpha / len(X)) * np.sum(term))
theta = temp
cost[i] = computeCost(X, y, theta)
return theta, cost
# 多变量线性回归
# 预处理步骤 - 特征归一化
def orgfunc(data2):
data2 = (data2 - data2.mean()) / data2.std()
data2.head()
# scikit-learn 的线性回归算法
from sklearn import linear_model
model = linear_model.LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
# 正规方程
def normalEqn(X, y):
theta = np.linalg.inv(X.T@X)@X.T@y # X.T@X 等价于 X.T.dot(X)
return theta
参考资料快照
- https://github.com/luweiagi/machine-learning-notes/blob/master/docs/perface/machine-learning-learning-path/machine-learning-learning-path.md
- https://github.com/luweiagi/machine-learning-notes/blob/master/docs/perface/machine-learning-perface/machine-learning-perface.md
- https://space.bilibili.com/29834628
- https://www.zhihu.com/people/liang-rong-24-62
- https://github.com/azataiot/DeepLearning-Notes
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1qf4y1x7kB/
- https://www.coursera.org/course/ml
- https://cs231n.Stanford.edu
- https://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.silver/web/Teaching.html
- https://b23.tv/eLlyiPI
- https://github.com/fengdu78/Coursera-ML-AndrewNg-Notes
- http://www.ai-start.com/ml2014/
- https://scruel.github.io/Notes-ML-AndrewNg/
- https://liumin.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125546056
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/71804c97123d
- https://github.com/pengsida/learning_research
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ys411472E
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1zx411g7gq
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Wv411h7kN?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1aE411o7qd?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nJ411z7fe
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1pb4y1s7hS/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=cd39e17f789bd6d503b915533f2c2237
- https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-030-93158-2
- https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html
- https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
- 机器学习 -- 大型语言模型简史:从 Transformers (2017) 到 DeepSeek-R1(2025) | 20 Feb 2025
- 机器学习 -- DALL·E 2 & 扩散模型 | 21 Dec 2024
- 机器学习 -- 学术论文解读系列(进行中) | 04 Oct 2024
- 机器学习 -- 经典论文 ViT (Vision Transformer) | 24 Jul 2024
- 机器学习 -- 跟李沐学 AI【论文精读】(进行中) | 09 Jul 2024
- 机器学习 -- Attention is all you need | 30 Jun 2024
- 机器学习笔记 -- 3Blue1Brown 深度学习 Deep Learning(已完成) | 29 Jun 2024
- 机器学习 -- 李宏毅 2021/2022 春机器学习课程(进行中) | 31 Aug 2023
- 机器学习 -- 实用机器学习 李沐(进行中) | 31 Aug 2023
- 机器学习 -- ChatGPT Prompt 提示词 吴恩达(进行中) | 28 Jul 2023
- 机器学习 -- 浙江大学 · 机器学习(已完成) | 12 Feb 2023
- 机器学习 -- 人工智能学习路线(进行中……) | 10 Feb 2023
- 机器学习 -- 北交 / 图像处理与机器学习(已完成) | 03 Dec 2022
- 机器学习笔记 -- 人工智能 机器学习 算法概览(已完成) | 13 Oct 2022
- 机器学习笔记 -- 神经网络内部发生了什么?深度学习可视化 | 13 Oct 2022
- 机器学习 -- 吴恩达机器学习 Review(已完成) | 31 Aug 2022
- 机器学习 -- 吴恩达深度学习(进行中) | 31 Aug 2022
- 机器学习 -- 吴恩达机器学习(已完成) | 31 Aug 2022
- 机器学习笔记 -- 神经网络和深度学习简史 | 26 Dec 2020
 .
.