图形学笔记 -- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门(光线追踪和动画)
十三、光线追踪(基本原理)Ray Tracing
- Whitted-Style Ray Tracing

Why Ray Tracing?
Light Rays Three ideas about light rays
- Light travels in straight lines (though this is wrong) 直线
- Light rays do not “collide” with each other if they cross (though this is still wrong) 不碰撞
- Light rays travel from the light sources to the eye (but the physics is invariant under path reversal - reciprocity). 可逆性
“And if you gaze long into an abyss, the abyss also gazes into you.” — Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (translated)
求射线和一个平面的交点?一个重心坐标,搞定,真的是神奇哦。
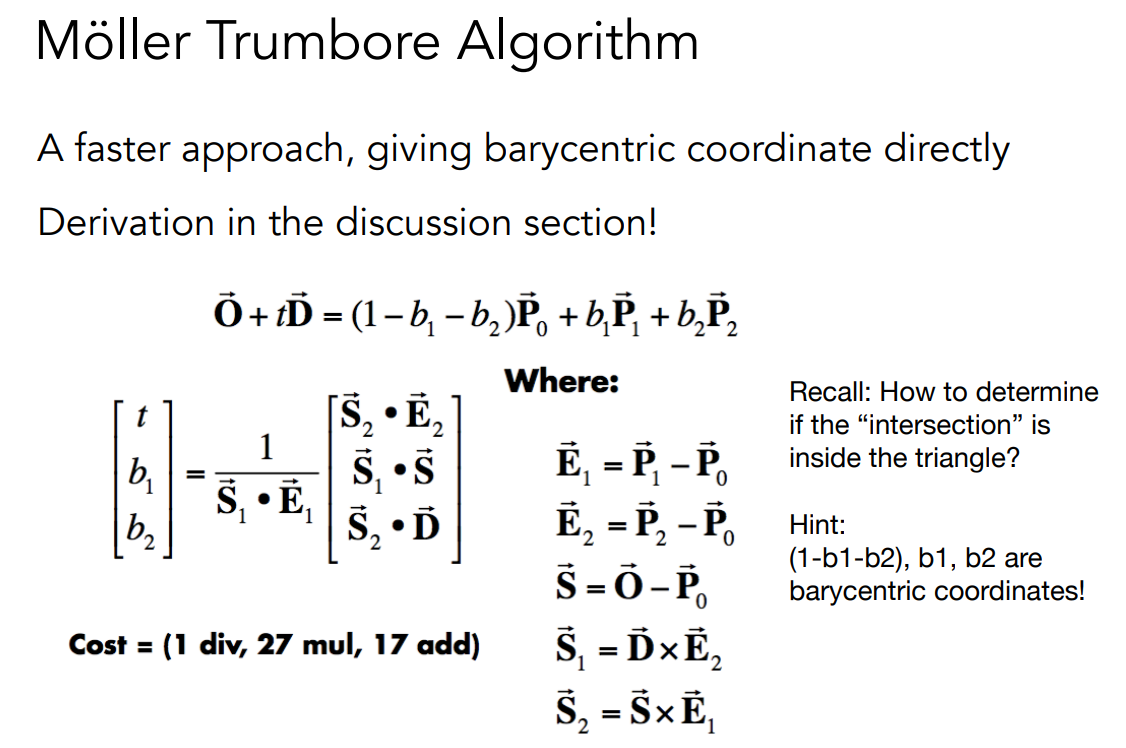
Möller Trumbore Algorithm
Axis-Aligned Bounding Box (AABB) (轴对齐包围盒)
- The ray enters the box only when it enters all pairs of slabs
- The ray exits the box as long as it exits any pair of slabs
- For the 3D box, tenter = max{tmin}, texit = min{tmax}
十四、光线追踪(加速结构)
Uniform Spatial Partitions (Grids)
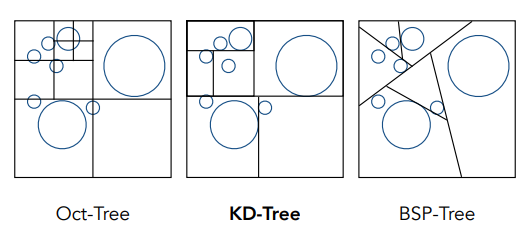
Spatial Partitioning Examples
Data Structure for KD-Trees
Internal nodes store
- split axis: x-, y-, or z-axis
- split position: coordinate of split plane along axis
- children: pointers to child nodes
- No objects are stored in internal nodes Leaf nodes store
- list of objects
Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH)
快速选择算法  其时间复杂度可以达到 \(O(n)\)。
网页里面的代码存在 bug,稍微改了改。^_^
其时间复杂度可以达到 \(O(n)\)。
网页里面的代码存在 bug,稍微改了改。^_^
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <assert.h>
template<typename T>
void qSwap(T arr[], int x, int y) {
if (x == y) return;
T temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[y];
arr[y] = temp;
}
template<typename T>
void qDebug(T arr[], int low, int high, int k, int size) {
printf("%d %d %d - ", low, high, k);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf(i == low ? "[" : " ");
printf("%d", arr[i]);
printf(i == high ? "]" : " ");
}
printf("\n");
}
// 在选出第 K 大的元素之后,我们也自然有了前 K 大的数,
// 因为在 K 右边的数都是比 K 大的,在 K 左边的数都是比 K 小的。
template<typename T>
T qSelect(T arr[], int low, int high, int k, int size) {
qDebug(arr, low, high, k, size);
if (low >= high) {
assert(k == low); // 断言断的是我们的代码没有 bug。
return arr[low];
}
int left = low;
int right = high + 1;
int key = arr[low];
while (true) {
/* 从左向右找比 key 大的值 */
while (arr[++left] < key) {
if (left == high) {
break;
}
}
/* 从右向左找比 key 小的值 */
while (arr[--right] > key) {
if (right == low) {
break;
}
}
if (left >= right) break;
/* 交换 left, right 对应的值 */
qSwap(arr, left, right);
}
/* 中枢值与 right 对应值交换 */
assert(arr[right] <= key);
// 左边都是比 key 小等的,右边都是比 key 大等的。
qSwap(arr, low, right);
// 从小到大排序的第 k 个元素。
if (right > k) {
return qSelect(arr, low, right - 1, k, size);
}
else if (right < k) {
return qSelect(arr, right + 1, high, k, size);
}
else {
return arr[right];
}
}
int compare(const void* a, const void* b) {
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
int* genArray(int size) {
int* ali = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
ali[i] = abs(rand()) % 10;
}
return ali;
}
void freeArray(int* ali) {
delete[] ali;
}
int maintest() {
int size = abs(rand()) % 8 + 1;
int* ali = genArray(size);
int k = abs(rand()) % size;
int result = qSelect(ali, 0, size - 1, k, size);
qsort(ali, size, sizeof(int), compare);
if (result != ali[k]) {
assert(result == ali[k]);
}
freeArray(ali);
printf("result - %d \n", result);
return 0;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
maintest();
}
return 0;
}
跑出来的示例:
0 1 0 - [7 4]
0 0 0 - [4] 7
result - 4
0 1 0 - [4 8]
result - 4
0 2 1 - [4 5 5]
1 2 1 - 4 [5 5]
1 1 1 - 4 [5] 5
result - 5
0 3 3 - [1 1 5 2]
2 3 3 - 1 1 [5 2]
result - 5
0 4 2 - [1 4 2 3 2]
1 4 2 - 1 [4 2 3 2]
1 3 2 - 1 [2 2 3] 4
result - 2
0 5 0 - [6 8 5 7 6 1]
0 2 0 - [6 1 5] 6 7 8
0 1 0 - [5 1] 6 6 7 8
0 0 0 - [1] 5 6 6 7 8
result - 1
0 5 3 - [2 7 9 5 4 3]
1 5 3 - 2 [7 9 5 4 3]
1 3 3 - 2 [4 3 5] 7 9
3 3 3 - 2 3 4 [5] 7 9
result - 5
0 2 0 - [3 3 4]
0 0 0 - [3] 3 4
result - 3
0 7 3 - [3 8 7 4 2 7 7 9]
2 7 3 - 2 3 [7 4 8 7 7 9]
2 4 3 - 2 3 [7 4 7] 7 8 9
2 3 3 - 2 3 [7 4] 7 7 8 9
result - 7
0 5 0 - [9 8 6 5 0 2]
0 4 0 - [2 8 6 5 0] 9
0 0 0 - [0] 2 6 5 8 9
result - 0
BVH Traversal
Intersect(Ray ray, BVH node) {
if (ray misses node.bbox) return;
if (node is a leaf node)
test intersection with all objs;
return closest intersection;
hit1 = Intersect(ray, node.child1);
hit2 = Intersect(ray, node.child2);
return the closer of hit1, hit2;
}
Spatial vs Object Partitions
Spatial partition (e.g.KD-tree)
- Partition space into non-overlapping regions 区域不交叠
- An object can be contained in multiple regions 一个物体可能在多个区域
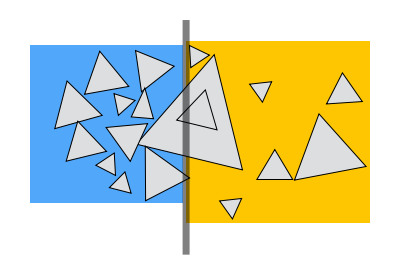
Object partition (e.g. BVH)
- Partition set of objects into disjoint subsets 根据物体分割
- Bounding boxes for each set may overlap in space 区域可能存在交叠
Whitted-Style 光线追踪算讲完了。
Basic radiometry(辐射度量学)
Advertisement: new topics from now on, scarcely covered in other graphics courses
- Radiant Flux 辐射通量 ? Radiant Energy and Flux (Power)
Definition: Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation. It is measured in units of joules, and denoted by the symbol:
\[Q[\mathrm{~J}=\text { Joule }]\]Definition: Radiant flux (power) is the energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time.
\[\Phi \equiv \frac{\mathrm{d} Q}{\mathrm{~d} t}[\mathrm{~W}=\text { Watt }][\operatorname{lm}=\text { lumen }]^{\star}\]功率 ?
-
Radiant Intensity 辐射强度 ? “Radiant Intensity” 发射出去多少光线。
-
Irradiance 辐 [射] 照度 ? “Irradiance” 接收到多少光线。
-
Radiance 辐 [射] 亮度 ? “Radiance” 传播过程中的度量。
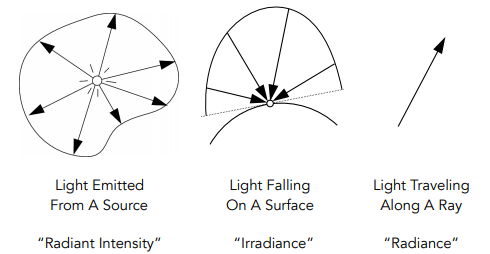
Important Light Measurements of Interest
十五、光线追踪(辐射度量学、渲染方程与全局光照)
辐射通量:单位立体角内的辐射通量
Radiant energy (barely used in CG)
- the energy of electromagnetic radiation \(Q[\mathrm{~J}=\text { Joule }]\)
Radiant flux (power)
- Energy per unit time \(\Phi \equiv \frac{\mathrm{d} Q}{\mathrm{~d} t}[\mathrm{~W}=\text { Watt }][\operatorname{lm}=\text { lumen }]\)
Radiant intensity
- power per unit solid angle \(I(\omega) \equiv \frac{\mathrm{d} \Phi}{\mathrm{d} \omega}\)
Solid Angle
- ratio of subtended area on sphere to radius squared \(\Omega=\frac{A}{r^{2}}\)
Irradiance
Definition: The irradiance is the power per unit area incident on a surface point. 辐照度:单位面积上的辐射通量
\[E(\mathbf{x}) \equiv \frac{\mathrm{d} \Phi(\mathbf{x})}{\mathrm{d} A}\] \[\left[\frac{\mathrm{W}}{\mathrm{m}^{2}}\right]\left[\frac{\mathrm{lm}}{\mathrm{m}^{2}}=\operatorname{lux}\right]\]Radiance
Radiance is the fundamental field quantity that describes the distribution of light in an environment
- Radiance is the quantity associated with a ray
- Rendering is all about computing radiance
Definition: The radiance (luminance) is the power emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a surface, per unit solid angle, per projected unit area.
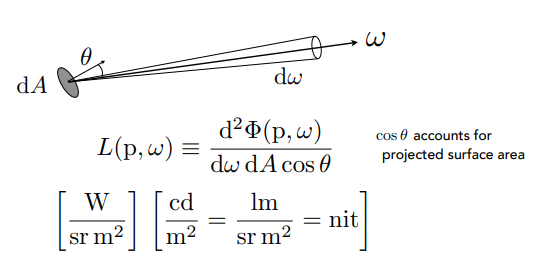
Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF)
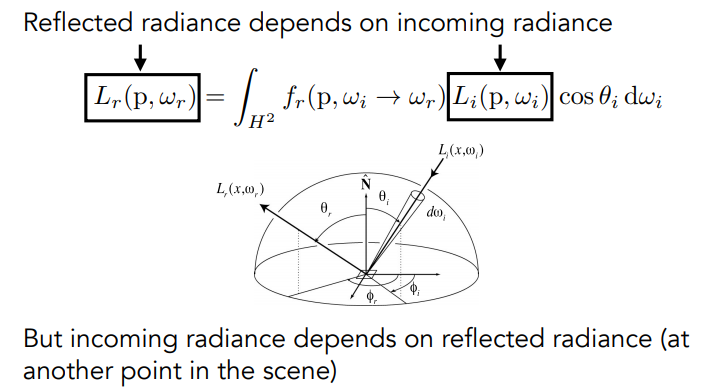
The Reflection Equation: Recursive Equation
概率: Continuous Case: Probability Distribution Function (PDF)
Conditions on p(x): \(p(x) \geq 0 \text { and } \int p(x) d x=1\)
Expected value of X: \(E[X]=\int x p(x) d x\)
十六、光线追踪(蒙特卡洛积分与路径追踪)
Monte Carlo estimator 基本蒙特卡洛估计器
\[F_{N}=\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \frac{f\left(X_{i}\right)}{p\left(X_{i}\right)}\] \[L_{o}\left(p, \omega_{o}\right)=L_{e}\left(p, \omega_{o}\right)+\int_{\Omega^{+}} L_{i}\left(p, \omega_{i}\right) f_{r}\left(p, \omega_{i}, \omega_{o}\right)\left(n \cdot \omega_{i}\right) \mathrm{d} \omega_{i}\]十七、材质与外观
Material == BRDF BRDF 的全名是 bidirectional reflectance distribution function
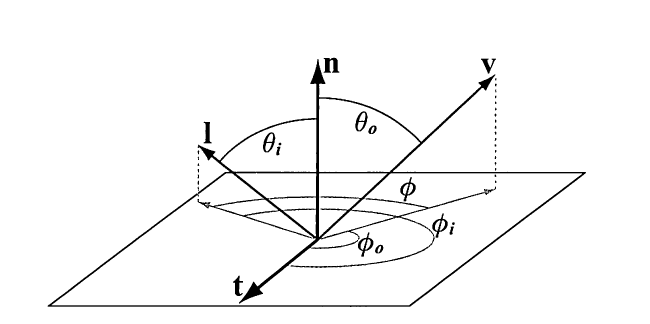
十八、高级光线传播与复杂外观建模
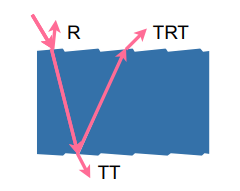
毛发渲染模型 Marschner model
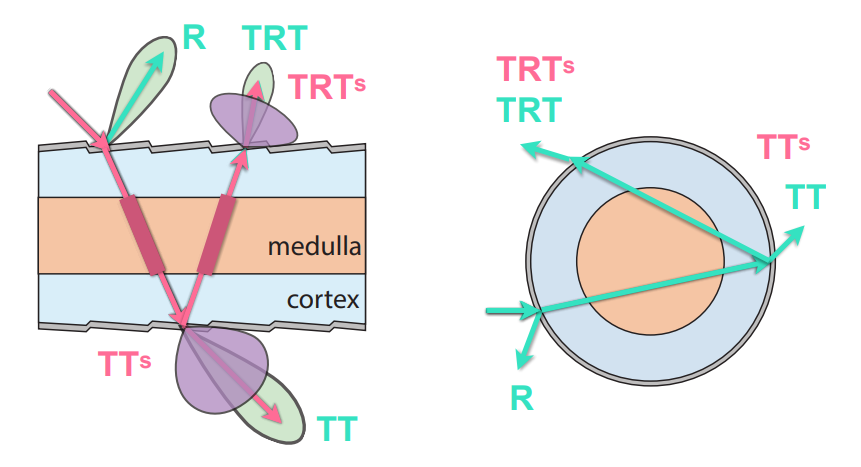
Double Cylinder Model — Lobes
相机与透镜
摄影入门,相机与透镜 的图形学原理。根据 闫令琪 课程整理。 照相机与透镜(光圈、快门和景深)
\[P\left(\theta, \phi, \lambda, t, V_{X}, V_{Y}, V_{Z}\right)\]- Can reconstruct every possible view, at every moment, from every position, at every wavelength
- Contains every photograph, every movie, everything that anyone has ever seen! it completely captures our visual reality! Not bad for a fXncWion«
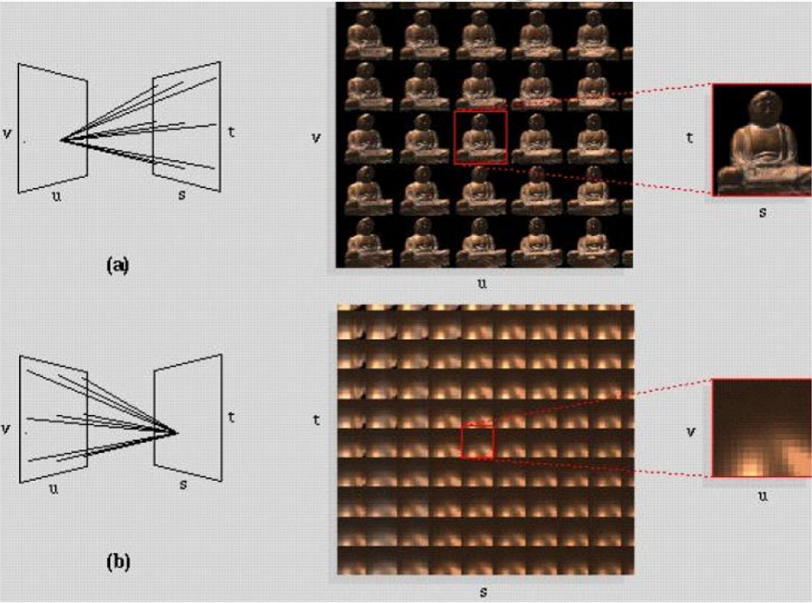
Lumigraph / Lightfield
光场、颜色与感知 Color and Perception
各种颜色空间是怎么推导来的?
400 纳米到 700 纳米。
What is Color?
- Color is a phenomenon of human perception; it is not a universal property of light
- Different wavelengths of light are not “colors”
动画与模拟(基本概念、质点弹簧系统、运动学)
Introduction to Computer Animation
- History
- Keyframe animation
- Physical simulation
- Kinematics
- Rigging
• Film: 24 frames per second • Video (in general): 30 fps • Virtual reality: 90 fps
逆运动学,采用梯度下降算法求解。
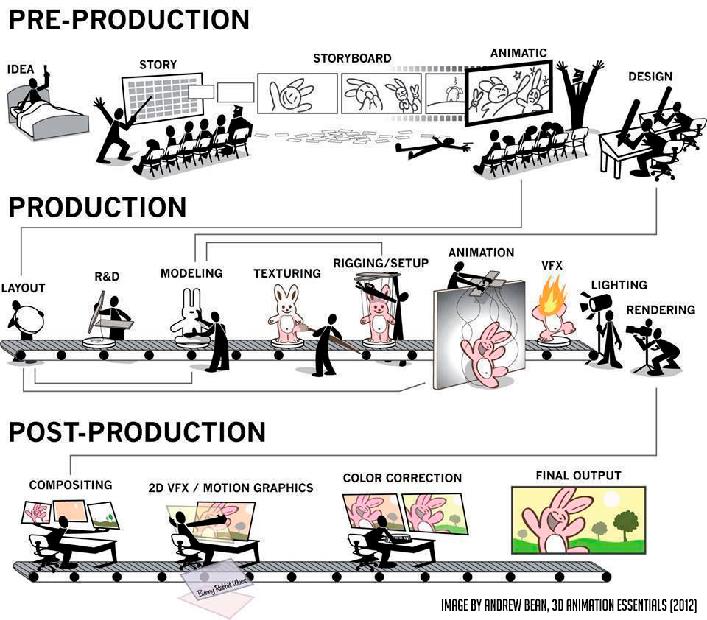
The Production Pipeline
动画与模拟(求解常微分方程,刚体与流体)
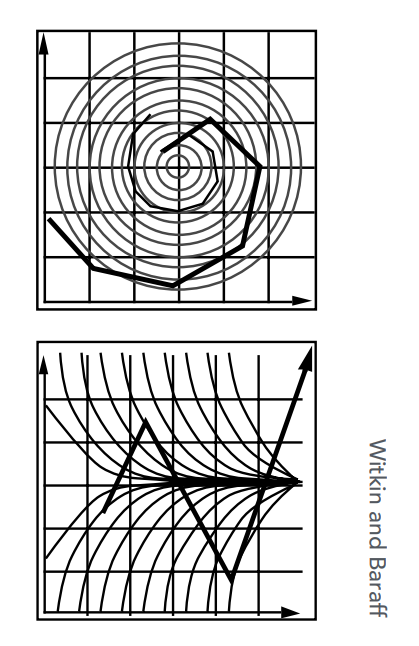
Instability of the Euler Method
Some Methods to Combat Instability
- Midpoint method / Modified Euler
- Average velocities at start and endpoint
- 采用中间的速度。
- Adaptive step size
- Compare one step and two half-steps, recursively, until error is acceptable
- 不断细分,直到误差小于一个特定值。
- Implicit methods
- Use the velocity at the next time step (hard)
- Implicit Euler Method
- Position-based / Verlet integration – Verlet 积分法
- Constrain positions and velocities of particles after time step
Runge-Kutta Families
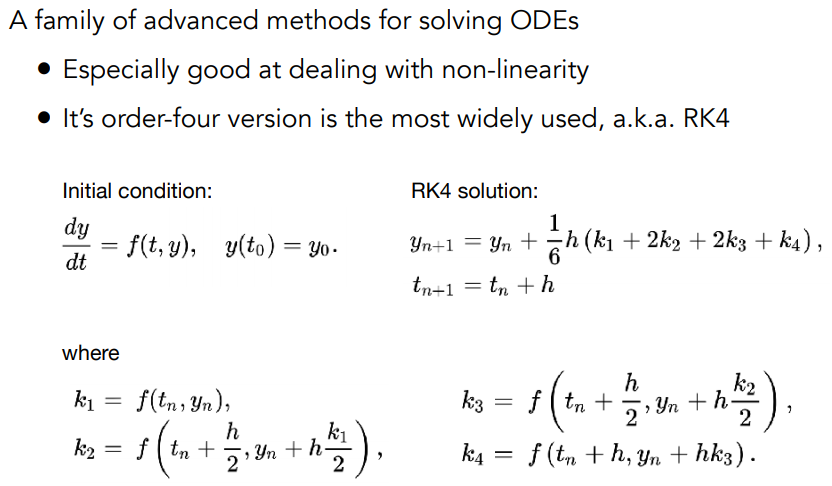
Runge-Kutta Families
This paper simplified the mass-spring model using the rigid stick to replace the spring connection of masses, and using the Verlet integration to calculate the position and speed of the mass. 在质点-弹簧模型的基础上,对织物模型进行进一步的简化。将连接质点的弹簧换成了刚性杆,同时采用 Verlet 积分法计算质点的位置和速度。
Rigid Body Simulation 刚体模拟
\[\frac{d}{d t}\left(\begin{array}{c} \mathrm{X} \\ \theta \\ \dot{\mathrm{X}} \\ \omega \end{array}\right)=\left(\begin{array}{c} \dot{\mathrm{X}} \\ \omega \\ \mathrm{F} / M \\ \Gamma / I \end{array}\right)\] \[\begin{aligned} &X: \text { positions } \\ &\theta: \text { rotation angle } \\ &\omega: \text { angular velocity } \\ &F: \text { forces } \\ &\Gamma: \text { torque } \\ &\text { I : momentum of inertia } \end{aligned}\]Fluid Simulation
Taichi 语言基础 刚体 液体 烟雾 弹塑性体 PIC/FLIP 法 Krylov-子空间求解器 预条件 无矩阵法 多重网格 弱形式与有限元 隐式积分器 辛积分器 拓扑优化 带符号距离场 自由表面追踪 物质点法 大规模物理效果渲染 现代处理器微架构 内存层级 并行编程 GPU 编程 稀疏数据结构 可微编程…

参考资料快照
- 图形学笔记 -- Color and Perception(颜色和感知) | 02 Oct 2021
- 图形学笔记 -- 摄影入门 · 照相机与透镜,光圈、快门和景深 | 23 Sep 2021
- 图形学笔记 -- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门(光线追踪和动画) | 01 Aug 2021
- 图形学笔记 -- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门 | 11 Jul 2021
 .
.