图形学笔记 -- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门
一、计算机图形学概述
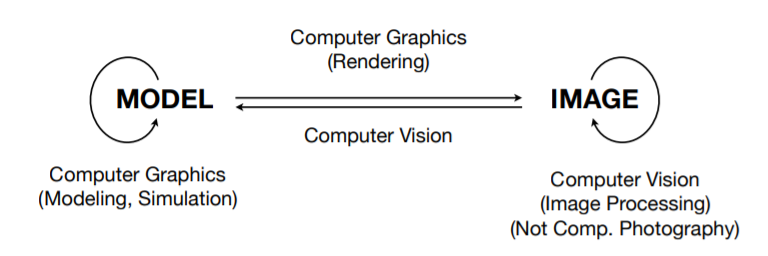
二、向量与线性代数
- Basic mathematics
- Linear algebra, calculus, statistics 线性代数、微积分、统计学
- Basic physics
- Optics, Mechanics 光学、力学
- Misc
- Signal processing 信号处理
- Numerical analysis 数值分析
-
And a bit of aesthetics 美感
-
Vector Normalization \(\hat{a}=\vec{a} /\|\vec{a}\|\)
-
默认竖着写: \(\mathbf{A}=\left(\begin{array}{l} x \\ y \end{array}\right)\)
-
点乘: \(\cos \theta=\hat{a} \cdot \hat{b}\)
-
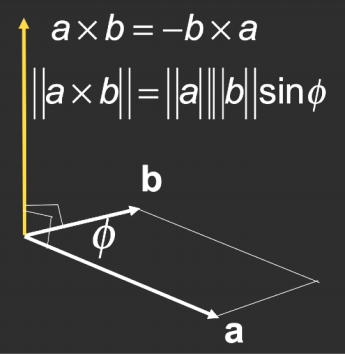
叉乘:
- Cross product is orthogonal to two initial vectors
- Direction determined by right-hand rule
- Useful in constructing coordinate systems (later)
-
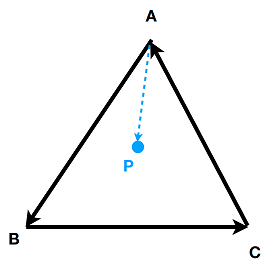
- Cross Product in Graphics 判断点是否三角形内部:
- 矩阵
- Associative and distributive
- \[(AB)C=A(BC)\]
- \[A(B+C) = AB + AC\]
- \[(A+B)C = AC + BC\]
- \[有交换律,没有交换律。\]
- \[(A B)^{T}=B^{T} A^{T}\]
三、变换(二维与三维)
- 正运动学:已知各关节 de 角度,求末端的位姿。
- 逆运动学:已知末端的位姿,求各关节的转角。
Add a third coordinate (w-coordinate)
- 2D point $=(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{y}, \mathbf{1})^{\top}$
- 2D vector $=(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{y}, \mathbf{0})^{\top}$
四、变换(模型、视图、投影)
这一章很精彩,讲了几个矩阵的推导过程。
\[\begin{aligned} &\mathbf{R}_{x}(\alpha)=\left(\begin{array}{cccc} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \cos \alpha & -\sin \alpha & 0 \\ 0 & \sin \alpha & \cos \alpha & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right) \\ &\mathbf{R}_{y}(\alpha)=\left(\begin{array}{cccc} \cos \alpha & 0 & \sin \alpha & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ -\sin \alpha & 0 & \cos \alpha & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right) \\ &\mathbf{R}_{z}(\alpha)=\left(\begin{array}{cccc} \cos \alpha & -\sin \alpha & 0 & 0 \\ \sin \alpha & \cos \alpha & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right) \end{aligned}\] \[\mathbf{R}_{x y z}(\alpha, \beta, \gamma)=\mathbf{R}_{x}(\alpha) \mathbf{R}_{y}(\beta) \mathbf{R}_{z}(\gamma)\]Rotation by angle $\alpha$ around axis $n$: \(\mathbf{R}(\mathbf{n}, \alpha)=\cos (\alpha) \mathbf{I}+(1-\cos (\alpha)) \mathbf{n} \mathbf{n}^{T}+\sin (\alpha) \underbrace{\left(\begin{array}{ccc} 0 & -n_{z} & n_{y} \\ n_{z} & 0 & -n_{x} \\ -n_{y} & n_{x} & 0 \end{array}\right)}_{\mathbf{N}}\)
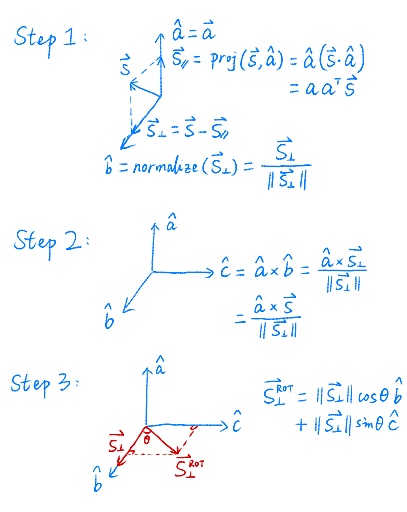
Rodrigues’ Rotation Formula
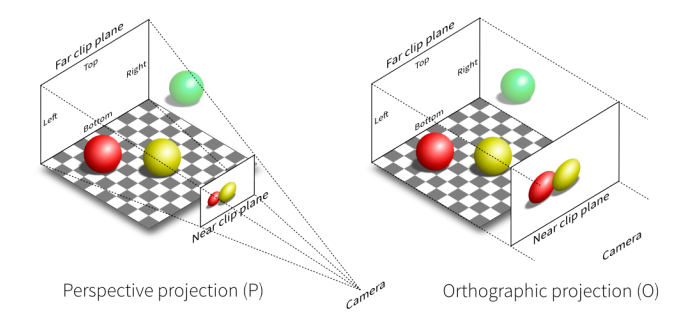
Perspective projection vs. orthographic projection
Translate (center to origin) first, then scale (length/width/height to 2).
正交投影: \(M_{\text {ortho }}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} \frac{2}{r-l} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \frac{2}{t-b} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \frac{2}{n-f} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{cccc} 1 & 0 & 0 & -\frac{r+l}{2} \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -\frac{t+b}{2} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -\frac{n+f}{2} \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]\)
\[M_{\text {persp }}=M_{\text {ortho }} M_{\text {persp } \rightarrow \text { ortho }}\]五、光栅化(三角形的离散化)
六、光栅化(深度测试与抗锯齿)
- Frequency Domain

十字的白线可以理解为周期延拓? 近视眼是离焦模糊,可以理解是低通(平均化)。
Convolution in the spatial domain is equal to multiplication in the frequency domain, and vice versa.
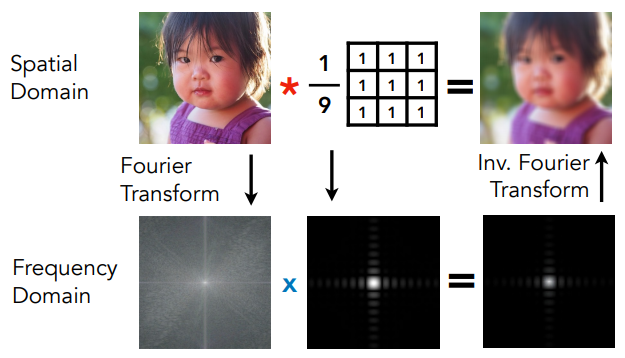
Convolution Theorem
时域的卷积等于频域的乘积。 时域的乘积等于频域的卷积。
How Can We Reduce Aliasing Error?
Option 1: Increase sampling rate
- Essentially increasing the distance between replicas in the Fourier domain
- Higher resolution displays, sensors, framebuffers…
- But: costly & may need very high resolution
Option 2: Antialiasing
- Making Fourier contents “narrower” before repeating
- i.e. Filtering out high frequencies before sampling
MSAA 本质是一个低通滤波的过程,保留低频信号,移除高频信号,避免频谱重复时发生混合,从而实现视觉抗锯齿。
No free lunch!
- What’s the cost of MSAA? Milestones (personal idea)
- FXAA (Fast Approximate AA) 后处理,匹配边界然后移除边界。先得到带有锯齿的图,然后通过一些图像匹配的方法找到这些锯齿边界,然后将这些边界换成没有锯齿的边界。属于图像的后期处理。
- TAA (Temporal AA) 时间抗锯齿,MSAA 在时间上采样。将采样点从单帧分布到多个帧上,使得每一帧并不需要多次采样增加计算量。 Super resolution / super sampling 超分辨率,超采样。
- From low resolution to high resolution
- Essentially still “not enough samples” problem
- DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) 小图拉大,细节通过深度学习猜出来。
七、着色(光照与基本着色模型)
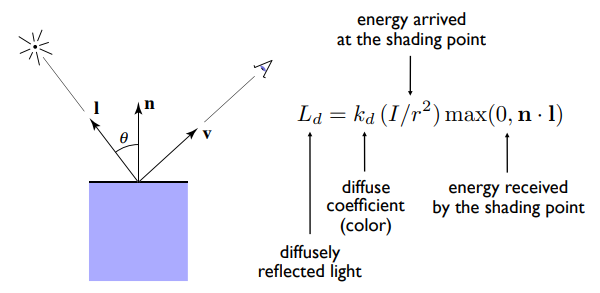
Lambertian (Diffuse) Shading
八、着色(着色频率、图形管线、纹理映射)
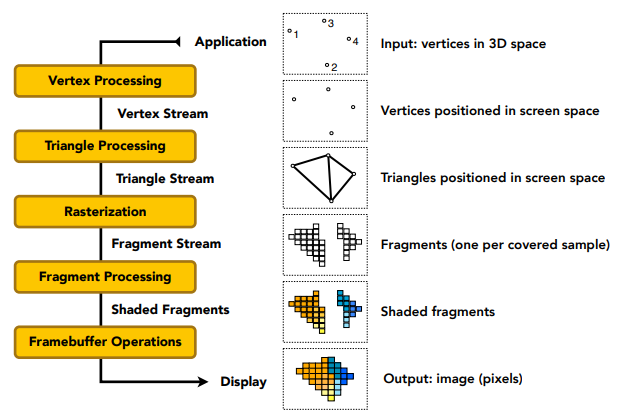
Graphics Pipeline

Unreal Engine Kite Demo (Epic Games 2015)
九、着色(插值、高级纹理映射)
- Barycentric Coordinates 重心坐标
- Mipmap
- Allowing (fast, approx., square) range queries
- 层与层之间再插值。 多 1/3 存储 ,Trilinear filtering: visualization of continuous D
- 各向异性过滤, 3 倍存储 Anisotropic Filtering
Nearest Point Sampling(最近点采样),Bilinear(双线性过滤)、Trilinear(三线性过滤)、Anisotropic Filtering(各向异性过滤)。
Trilinear filtering: visualization of continuous D
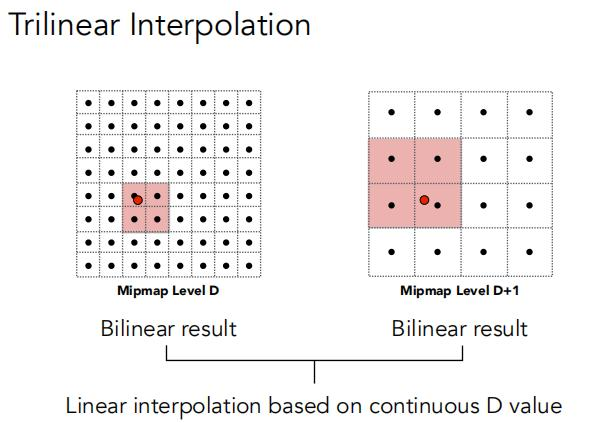
三线性插值
Anisotropic Filtering 矩形区域
- Ripmaps and summed area tables
- Can look up axis-aligned
- rectangular zones
- Diagonal footprints still a problem
- EWA filtering 各种方向的椭圆
- Use multiple lookups
- Weighted average
- Mipmap hierarchy still helps
- Can handle irregular footprints
十、几何(基本表示方法)
Bump / Normal mapping 法线贴图
How to perturb the normal (in 3D)
- Original surface normal n(p) = (0, 0, 1)
- Derivatives at p are
- dp/du = c1 * [h(u+1) - h(u)]
- dp/dv = c2 * [h(v+1) - h(v)]
- Perturbed normal is n = (-dp/du, -dp/dv, 1).normalized()
- Note that this is in local coordinate!
- More will be elaborated in FAQ of HW3
Implicit Representations - Pros & Cons 隐式表达 - 优点和缺点
Pros:
- compact description (e.g., a function) 简洁的描述
- certain queries easy (inside object, distance to surface) 某些查询很简单
- good for ray-to-surface intersection (more later) 适用于光线与曲面相交
- for simple shapes, exact description / no sampling error 对于简单形状,精确描述 / 无采样错误
- easy to handle changes in topology (e.g., fluid) 易于处理拓扑变化(如流体)
Cons:
- difficult to model complex shapes 难以模拟复杂形状
符号距离函数(sign distancefunction),简称 SDF,又可以称为定向距离函数(oriented distance function),在空间中的一个有限区域上确定一个点到区域边界的距离并同时对距离的符号进行定义:点在区域边界内部为正,外部为负,位于边界上时为 0。
from 
十一、几何(曲线与曲面)
Baskerville font - represented as piecewise cubic Bézier curves
\[\mathbf{b}^{n}(t)=\mathbf{b}_{0}^{n}(t)=\sum_{j=0}^{n} \mathbf{b}_{j} B_{j}^{n}(t)\]Bernstein Polynomials:
\[B_{i}^{n}(t)=\left(\begin{array}{l} n \\ i \end{array}\right) t^{i}(1-t)^{n-i}\]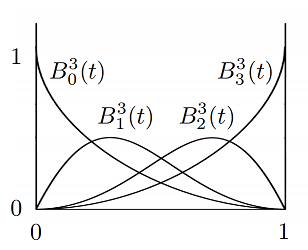
Affine transformation property
- Transform curve by transforming control points 控制点仿射变换
Convex hull property 凸包性质
- Curve is within convex hull of control points
- BTW: What’s a Convex Hull 曲线一定在凸包内
Piecewise Bézier Curves 逐段定义
Spline 样条。
十二、几何(网格处理)、阴影图
Quadric Error Metrics 二次误差度量
- Shadow Mapping
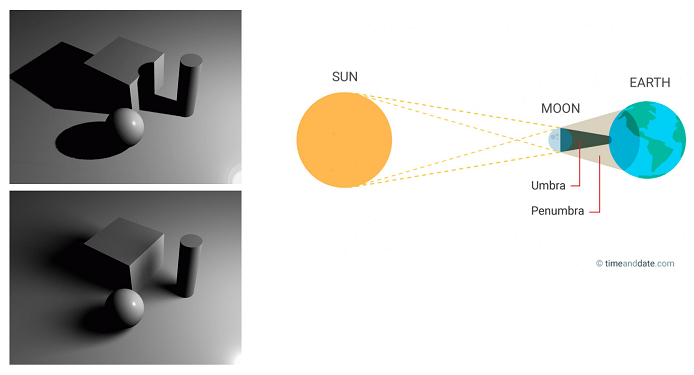
Hard shadows vs. soft shadows
参考资料快照
- https://mathpix.com/
- https://sites.cs.ucsb.edu/~lingqi/teaching/games101.html
- https://sites.cs.ucsb.edu/~lingqi/teaching/games202.html
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1X7411F744
- https://blog.csdn.net/wangjiangrong/article/details/114322213
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41368247/article/details/106194092
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/av97306984/
- 图形学笔记 -- Color and Perception(颜色和感知) | 02 Oct 2021
- 图形学笔记 -- 摄影入门 · 照相机与透镜,光圈、快门和景深 | 23 Sep 2021
- 图形学笔记 -- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门(光线追踪和动画) | 01 Aug 2021
- 图形学笔记 -- GAMES101: 现代计算机图形学入门 | 11 Jul 2021
 .
.