编程与调试 C++ -- OpenCL & CUDA 初探
OpenCL 是一个小而美的东西,比 OpenGL 要简单很多,妙不可言。( ̄▽ ̄)" OpenGL 需要图形学的知识储备,OpenCL 不太需要。
并行计算行情。
- CPU
- 首先是指令集优化:SIMD (SSE, AVX, NEON)
- 然后多线程跑:
- OpenMP 标准
- intel 搞的 TBB, oneTBB 等。
- Intel IPP tbb 加速

- Intel 将 TBB、IPP 等加速库集成到了 oneAPI 库中,所以可以直接安装 oneAPI,源码如下 https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneTBB
- GPU
- NVIDIA 搞的 CUDA
- OpenCL
标准
- Unlike 'GPU-only' APIs, such as Vulkan, OpenCL enables use of a diverse range of accelerators including multi-core CPUs, GPUs, DSPs, FPGAs and dedicated hardware such as inferencing engines.
- DirectX 搞的 DirectCompute
- 微软尝试从 C++ 语言级别搞的 C++ AMP
- 机器学习多为 CUDA 而 挖矿程序多为 CUDA 和 OpenCL。
眼睛能看到的是 OpenGL(Open Graphics Library),耳朵能听到的是 OpenAL(Open Audio Library),后来发现显卡可以用于通用计算,于是乎有了 OpenCL(Open Computing Language)。 OpenCL 和 OpenGL 都能用于操作 GPU,但是前者主要用于通用计算,而后者主要用于图像渲染。
clEnqueueMapBuffer / clEnqueueMapImage
clEnqueueMapBuffer / clEnqueueMapImage 用于访问内存对象的 OpenCL 机制,而不是使用 clEnqueueRead / Write。 我们可以将设备上的内存对象映射到主机上的内存区域。一旦我们映射了对象,我们就可以随意读 / 写或修改。 Read / Write 缓冲器和 clEnqueueMapBuffer 之间的一个更差的是 map_flags 参数。 如果 map_flags 设置为 CL_MAP_READ,映射的内存将是只读的,如果它被设置为 CL_MAP_WRITE 映射的内存将只写, 如果你想同时读取 + 写入然后再进行标志 CL_MAP_READ | CL_MAP_WRITE。 与读 / 写 fns 相比,内存映射需要三步过程:
- 使用 clEnqueueMapBuffer 映射内存。
- 通过 memcpy 将内存从设备传输到主机或从主机传输。
- 使用 clEnqueueUnmapObject 取消映射。 人们普遍认为,与常规读 / 写相比,内存映射可以显着提高性能,请参见此处: what's faster - AMD devgurus forum link 如果要复制图像或矩形区域的图像,则也可以使用 clEnqueueMapImage 调用。 参考文献: OpenCL in Action Heterogeneous computing with OpenCL Devgurus forum
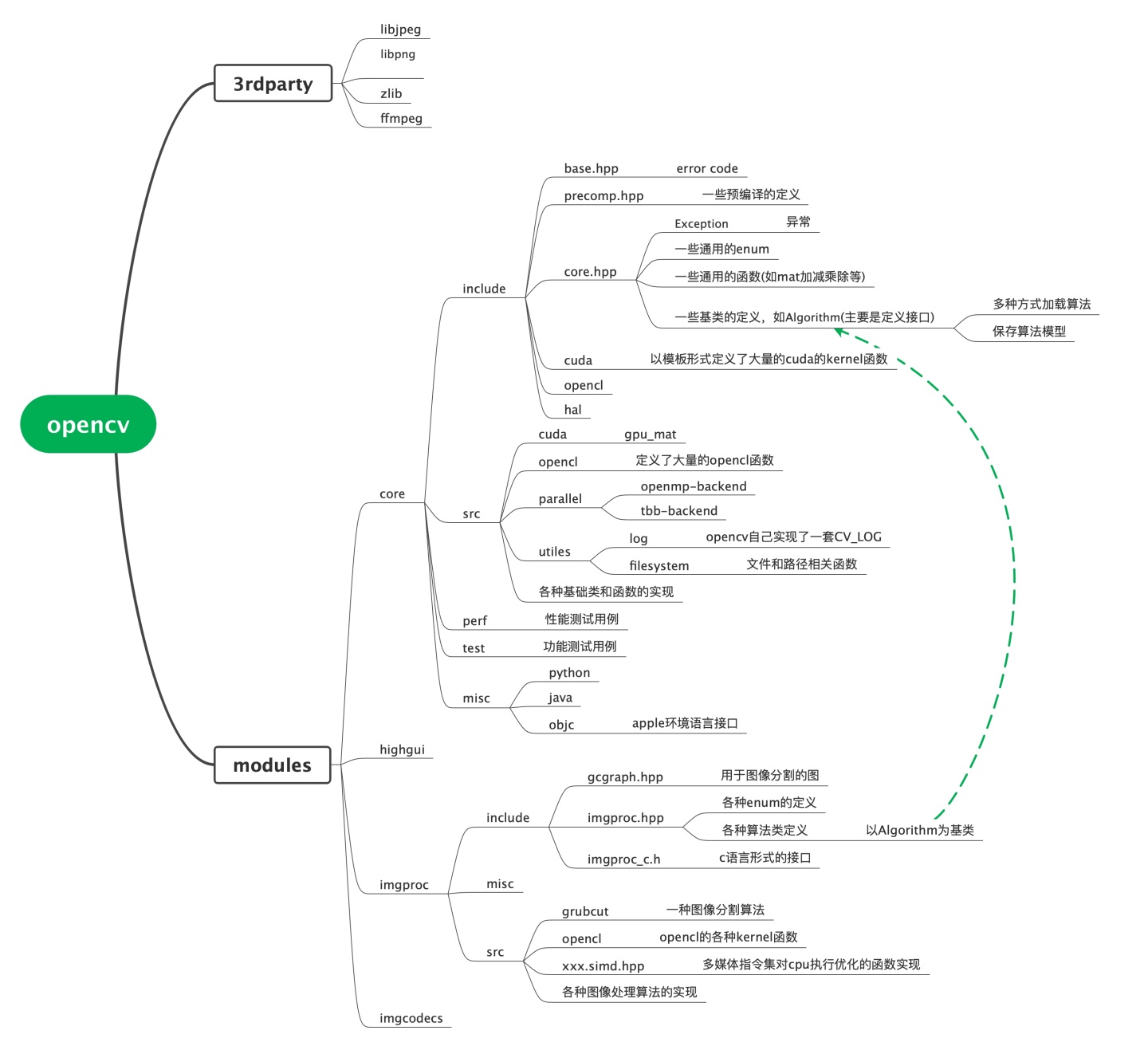
OpenCV Intel 的 IPP
- Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives (Intel® IPP)
- IPP(Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives,英特尔(R)集成性能原件)
- OpenCV 使用优化了的 C 和 C++ 代码实现。它对 IPP 不存在任何依赖。 但如果安装了 IPP,那么 OpenCV 将会通过自动载入 IPP 动态链接库来获取 IPP 的优势,来提升速度。
CV_EXPORTS_W void resize( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
Size dsize, double fx = 0, double fy = 0,
int interpolation = INTER_LINEAR );
- 会优先使用 OpenCL 实现
__kernel void resizeLN - 其次会使用 hal 的实现
目前 hal 层的 cv_hal_resize 默认并没有实现 - 再次会使用 Intel 的 IPP 库中的 ipp_resize
- 再次会使用 simd 汇编加速
- 如果 cpu 支持 avx2,会调用给予 avx2 多媒体指令集优化的函数
- 支持两个编译宏
CV_TRY_AVX2和CV_TRY_SSE4_1 CV_CPU_SSE4_1CV_CPU_SSE4_2CV_CPU_FP16CV_CPU_AVX- 源码 resize.avx2.cpp,resize.sse4_1.cpp
- 最后会有一个没有加速的 resize 原型实现。
OpenCV 关于 GPU 的具体优化实现基本都是用的 OpenCL。 高性能计算方面:多线程,cuda/opencl, simd。
- opencv 中的多线程加速
- 实现了两种 backend parallel_for.tbb.hpp 和 parallel_for.openmp.hpp
- 在 core/utility.hpp 里
// 获取当前使用的 ParallelForBackend,omp 或者 tbb CV_EXPORTS void parallel_for_(const Range& range, const ParallelLoopBody& body, double nstripes=-1.);
OpenCL 图片对象,支持 RGBA,就是不支持 R8G8B8,因为这个不是 4 字节对齐的,对性能不利,所以都没有支持!额……
cl_image_format getImageFormat(int depth, int cn, bool norm) {
cl_image_format format;
static const int channelTypes[] = {
CL_UNSIGNED_INT8, CL_SIGNED_INT8, CL_UNSIGNED_INT16, //
CL_SIGNED_INT16, CL_SIGNED_INT32, CL_FLOAT, //
-1, CL_HALF_FLOAT};
static const int channelTypesNorm[] = {
CL_UNORM_INT8, CL_SNORM_INT8, CL_UNORM_INT16, //
CL_SNORM_INT16, -1, -1, //
-1, -1};
// CL_RGB has no mappings to OpenCV types because CL_RGB can only be used with
// CL_UNORM_SHORT_565, CL_UNORM_SHORT_555, or CL_UNORM_INT_101010.
static const int channelOrders[] = {-1, CL_R, CL_RG, /*CL_RGB*/ -1, CL_RGBA};
int channelType = norm ? channelTypesNorm[depth] : channelTypes[depth];
int channelOrder = channelOrders[cn];
format.image_channel_data_type = (cl_channel_type)channelType;
format.image_channel_order = (cl_channel_order)channelOrder;
return format;
}
bool isFormatSupported(cl_image_format format) {
// Figure out how many formats are supported by this context.
cl_uint numFormats = 0;
cl_int err = clGetSupportedImageFormats(m_context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE, CL_MEM_OBJECT_IMAGE2D, //
numFormats, NULL, &numFormats);
if (err != CL_SUCCESS) {
return false;
}
if (numFormats > 0) {
cl_image_format* formats = new cl_image_format[numFormats];
err = clGetSupportedImageFormats(m_context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE, CL_MEM_OBJECT_IMAGE2D, //
numFormats, formats, NULL);
if (err != CL_SUCCESS) {
delete[] formats;
return false;
}
for (cl_uint i = 0; i < numFormats; ++i) {
if (!memcmp(&formats[i], &format, sizeof(format))) {
delete[] formats;
return true;
}
}
delete[] formats;
}
return false;
}
oneAPI 组件简介
https://0cch.com/2022/03/08/oneapi-summary/
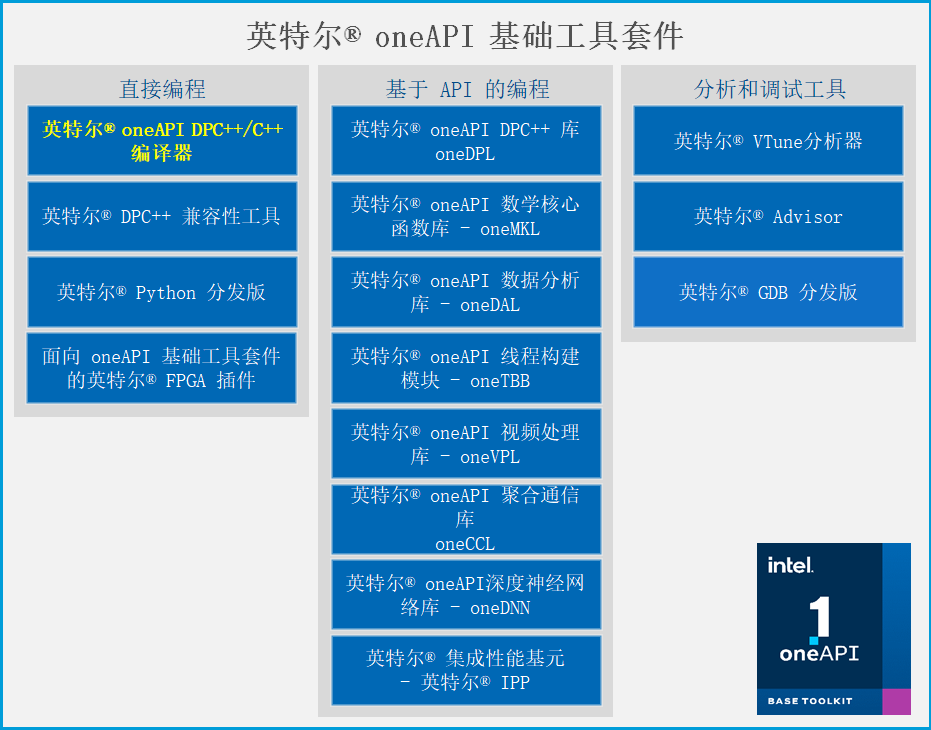
Vtune ,这个工具就厉害了,我想做过性能优化的朋友肯定是用过的。这个工具在做性能优化方面并不局限于异构程序,其实很早之前我就接触过它了。 它可以对程序性能的缺陷做非常系统的分析,包括 IO,线程、内存、指令集的使用等等, 分析的粒度可以从指令到代码行再到函数块,支持的架构从 CPU、GPU 到 FPGA。
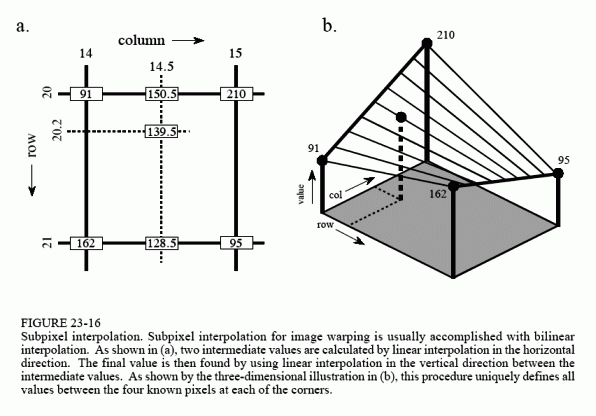
OpenCV —— 双线性插值(Bilinear interpolation)
- 源图像和目标图像几何中心的对齐。
- 将浮点运算转换成整数运算
- 浮点运算→→整数运算→→”« 左右移按位运算”
- 图像处理界双线性插值算法的优化
- 考虑到图像的特殊性,他的像素值的计算结果需要落在 0 到 255 之间,最多只有 256 种结果,由上式可以看出,一般情况下,计算出的 f(x,y) 是个浮点数,我们还需要对该浮点数进行取整。因此,我们可以考虑将该过程中的所有类似于 1-x、1-y 的变量放大合适的倍数,得到对应的整数,最后再除以一个合适的整数作为插值的结果。
// opencl_kernel_set.buildopts.txt
-D dstT=uchar3 -D rowsPerWI=4 -D dstST=uchar4 -D dstT1=uchar -D cn=3
CV_OCL_RUN(_src.dims() <= 2 && _dst.isUMat() && _src.cols() > 10 && _src.rows() > 10,
ocl_resize(_src, _dst, dsize, inv_scale_x, inv_scale_y, interpolation))
// opencl_kernel_resizeLN.buildopts.txt
__kernel void resizeLN(__global const uchar * srcptr, int src_step, int src_offset, int src_rows, int src_cols,
__global uchar * dstptr, int dst_step, int dst_offset, int dst_rows, int dst_cols,
float ifx, float ify);
// INTER_LINEAR resizeLN 15000,0,2812,5000/12000,0,2249,4000/1.25,1.25
// INTER_LINEAR resizeLN 300,0,100,100/240,0,80,80/1.25,1.25
// -D INTER_LINEAR -D depth=0 -D T=uchar3 -D T1=uchar -D WT=int3 -D convertToWT=convert_int3 -D convertToDT=convert_uchar3_sat -D cn=3 -D INTER_RESIZE_COEF_BITS=11
// -D INTER_LINEAR -D depth=0 -D T=uchar3 -D T1=uchar -D WT=int3 -D convertToWT=convert_int3 -D convertToDT=convert_uchar3_sat -D cn=3 -D INTER_RESIZE_COEF_BITS=11
static bool ocl_resize( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, Size dsize,
double fx, double fy, int interpolation)
{
int wdepth = std::max(depth, CV_32S), wtype = CV_MAKETYPE(wdepth, cn);
k.create("resizeLN", ocl::imgproc::resize_oclsrc,
format("-D INTER_LINEAR -D depth=%d -D T=%s -D T1=%s "
"-D WT=%s -D convertToWT=%s -D convertToDT=%s -D cn=%d "
"-D INTER_RESIZE_COEF_BITS=%d",
depth, ocl::typeToStr(type), ocl::typeToStr(depth), ocl::typeToStr(wtype),
ocl::convertTypeStr(depth, wdepth, cn, buf[0]),
ocl::convertTypeStr(wdepth, depth, cn, buf[1]),
cn, INTER_RESIZE_COEF_BITS));
if (k.empty())
return false;
k.args(ocl::KernelArg::ReadOnly(src), ocl::KernelArg::WriteOnly(dst),
(float)inv_fx, (float)inv_fy);
}
缓存:
- C:\Users\ADMIN\AppData\Local\Temp\opencv\4.5\opencl_cache
32-bit–Intel_R__Corporation–Intel_R__HD_Graphics_630–27_20_100_9168
core–copyset_f8f028f1776dc5c98bf03411d3b72318.bin -
C:\Users\ADMIN\AppData\Local\Temp\opencv\4.5\opencl_cache
32-bit–Intel_R__Corporation–Intel_R__HD_Graphics_630–27_20_100_9168
imgproc–resize_292f623900ce0dbfd5b5eb23a3c7c5bd.bin - C:\Users\ADMIN\AppData\Local\Temp\fastcl
32-bit–Intel_R__Corporation–Intel_R__HD_Graphics_630–27_20_100_9168
resize.cl–resizeLN_0x4ebcc29cb1fbc17c.bin
CL_TARGET_OPENCL_VERSION
/* Detect which version to target */
#if !defined(CL_TARGET_OPENCL_VERSION)
#pragma message("cl_version.h: CL_TARGET_OPENCL_VERSION is not defined. Defaulting to 300 (OpenCL 3.0)")
#define CL_TARGET_OPENCL_VERSION 300
#endif
/* cl_device_type - bitfield */
#define CL_DEVICE_TYPE_DEFAULT (1 << 0)
#define CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU (1 << 1)
#define CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU (1 << 2)
#define CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ACCELERATOR (1 << 3)
#ifdef CL_VERSION_1_2
#define CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CUSTOM (1 << 4)
#endif
#define CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL 0xFFFFFFFF
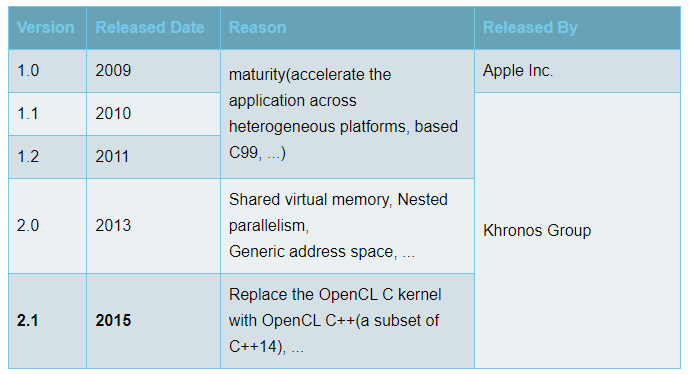
- OpenCL 2.0 异构计算 [第三版] (Heterogeneous Computing with OpenCL 2.0)
- OPENCL:并行世界的桥梁
- OPENCL:从朴素到更具深度的编程
void test() {
const cl_uint num_entries = 100;
const size_t param_value_size = 100;
cl_platform_id platforms[num_entries];
cl_uint num_platforms = 0;
clGetPlatformIDs(num_entries, platforms, &num_platforms);
for (int i = 0; i < num_platforms; i++) {
cl_platform_id platform = platforms[i];
cl_platform_info param_name = CL_PLATFORM_NAME;
char param_valuep[param_value_size];
size_t param_value_size_ret = 0;
clGetPlatformInfo(platform,
param_name,
param_value_size,
param_valuep,
¶m_value_size_ret);
cl_device_type device_type = CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL;
cl_device_id devices[num_entries];
cl_uint num_devices = 0;
clGetDeviceIDs(platform,
device_type,
num_entries,
devices,
&num_devices);
for (int j = 0; j < num_devices; j++) {
cl_device_id device = devices[j];
cl_device_info param_name = CL_DEVICE_NAME;
char param_valued[param_value_size];
size_t param_value_size_ret = 0;
clGetDeviceInfo(device,
param_name,
param_value_size,
param_valued,
¶m_value_size_ret);
param_value_size_ret = 0; //
}
}
}
Intel(R) OpenCL HD Graphics Intel(R) HD Graphics 630
存储模型
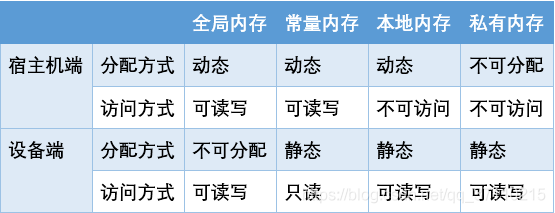
OpenCL 将设备中的内部存储器抽象成四层结构的存储模型:
- 全局内存(global memory) :同一个工作空间内的所有工作节点都可以进行读写,宿主机可以对其进行初始化,特点是存储容量大、访问速度慢。
- 常量内存(constant memory) :工作空间内所有工作节点都可以进行读操作,却不能进行写操作。由宿主机进行初始化,在 kernel 执行过程中保持不变。
- 本地内存(local memory) :同一个工作组中所有的工作节点都可以进行读写操作,对其他工作组内的工作节点不可见,不可以通过宿主机进行初始化。
- 私有内存(private memory) :工作节点的专属内存,对其他工作节点完全不可见,只能通过内核程序分配。
下表描述了宿主机和设备对内存的的分配和访问规则。
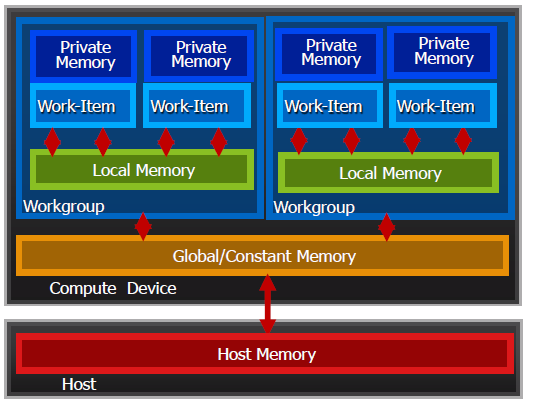
- 私有内存 (Private Memory)
- 每个工作项
- 局部内存 (Local Memory)
- 工作组内共享
- 全局 / 常量内存 (Global/Constant Memory)
- 对所有工作组可见
- 主机内存 (Host Memory)
- 在 CPU 上内存管理是显式的,你必须搬移数据从 host -> global -> local … ,然后返回。
在运行 OpenCL 应用时,宿主机需要将待处理的数据送到 OpenCL 设备,OpenCL 设备运算完成后需要把结构返回给宿主机,这就需要在宿主机与 OpenCL 设备之间进行数据交互,这种交互有两种方式:拷贝数据法和内存映射法。 OpenCL 规定了一个松散的内存模型,它不保证所有的工作节点访问的内存状态是一致的,它只规定在一个工作节点内部访问内存必须是一致的;在工作组内,可以通过同步点来保证组内节点的内存访问一致性。在不同工作组的访问内存一致性上,OpenCL 不提供任何保证。
OpenCL vs CUDA
OpenCL 和 nVidia CUDA 很像。
| CUDA | OpenCL |
|---|---|
| Thread | Work-item |
| Thread block | Work-group |
| global memory | global memory |
| constant memory | constant memory |
| shared memory | local memory |
| local memory | private memory |
| Grid size | Global range |
| Block size | Local range |
| __global__ | kernel |
| gridDim.x | get_num_groups(0) |
| blockDim.x | get_local_size(0) |
| blockIdx.x | get_group_id(0) |
| threadIds.x | get_local_id(0) |
| __syncthreads | barrier() |
| warp | no equivalent |
OpenCL 基本原理
- 准备 OpenCL 源码(C99)然后给 OpenCL。
- OpenCL 针对目标设备,编译源码。
- 向目标设备传输数据。(内存 到 显存)
- 在数据上运行 kernel。(GPU 运行)
- 把数据拖回来。(显存 到 内存)
OpenCL C++ 伪码
#include <cl/cl.hpp>
#include <vector>
using namespace cl;
using namespace std;
int main(int, char**)
{
Platform platform = Platform::getDefault();
vector<Device> devices;
platform.getDevices(CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ALL, &devices);
Context context(devices[0]);
CommandQueue queue(context, devices[0]);
Program program(context, "OpenCL C code goes here...");
program.build();
auto kernel = make_kernel<Buffer, Buffer>(program, "example_kernel");
const static int Size = 1000000;
vector<int> inputData(Size, 0), outputData(Size, 0);
Buffer inputBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY, Size * sizeof(int));
Buffer outputBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY, Size * sizeof(int));
// 发送数据
queue.enqueueWriteBuffer(inputBuffer, false, 0, Size * sizeof(int), inputData.data());
// 运行 kernel
kernel(EnqueueArgs(queue, NDRange(Size)), inputBuffer, outputBuffer);
// 拖回数据
queue.enqueueReadBuffer(outputBuffer, false, 0, Size * sizeof(int), outputData.data());
queue.finish();
return 0;
}
内核程序 OpenCL C
kernel void example_kernel(global int * input, global int * output)
{
int worker_id = get_global_id(0);
output[worker_id] = input[worker_id] + 10 + worker_id;
}
#define MACRO(a, b) a + b
bool function(int a)
{
float4 vector_type(0, 1, 2, 3); // 有的支持 SIMD
vector_type *= 2;
float v = vector_type.x; // 和 OpenGL 有点类似
float2 v2; float8 v8; float16 v16;
uchar uc; uint ui;
local bool local_buffer[256]; // local 内存不能初始化。
int lid = get_local_id(0);
if (lid < 256)
local_buffer[lid] = (uc8.S1 == uc);
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
if (lid < 256 && lid > 1)
return local_buffer[lid - 1];
return false;
}
OpenCL 性能优化
- 提前编译一次,再多次使用。
- 数据传输,只传必要的,只需要的时候才传。
- 运算能力往往高于带宽,kernel 拷贝到 local array 快于读取 global memory。
- Global data access Devices generally have more compute power than they have global memory bandwith kernels that read multiple values from global memory can be accelerated by copying the data in a local array
- 简单的多个 kernels 序列,性能不如一个大 kernel 直接一次运算。超大 kernel 可能会超出 硬件能力。
- A sequence of simple kernels will perform less than one kernel doing all the calculations at once. But a very big kernel can suffer from private or local memory exhaustion on some devices and will have less performance (this is usually not a problem except for very complex algorithms).
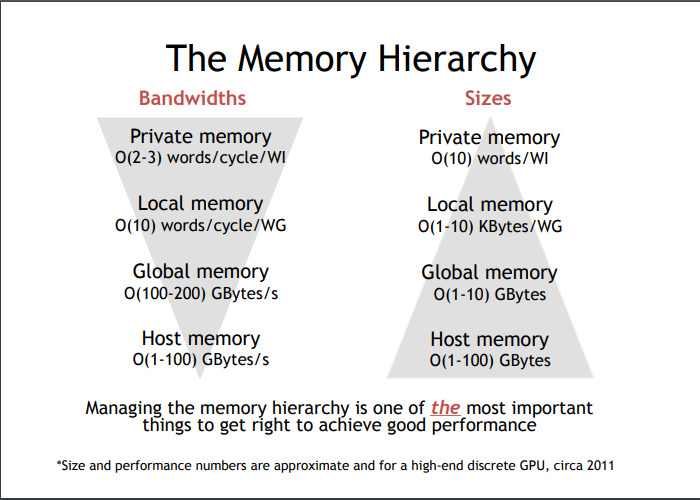
- GPU 内存与 CPU 内存有所区别。利用 OpenCL 进行程序性能优化的主要目标,是确保最大化带宽,而非像在 CPU 上一样缩短延迟。
- 存储访问的本质,对于总线利用的效率影响巨大。总线使用率低即意味着运行速度低。
- 要改善代码的性能,存储访问最好是相干的。此外,最好也要避免库冲突。
- 硬件规格(总线宽度、存储库数量,以及可以合并为单一相干访问的线程数量)请见供应商提供的相关文档。
性能对比
实现图片模糊,对比性能。
E:\kpdf\fastimage\fastapp-turbo\gpuip\build\test\Release\test_performance.exe E:\kpdf\fastimage\fastapp-turbo\gpuip\examples\images\bridge.exr E:\kpdf\fastimage\fastapp-turbo\gpuip\examples\kernels\
---------------------------------------------------------------
| LERP |
---------------------------------------------------------------
CPU: 33.6 ms.
CPU MT: 216.8 ms.
OpenCL: 4.5 ms, Process 0.8 ms (16.8%), Copy 3.7 ms (83.2%)
GLSL: 23.8 ms, Process 0.7 ms (2.8%), Copy 23.1 ms (97.2%)
---------------------------------------------------------------
| BOX BLUR |
---------------------------------------------------------------
CPU: 3491.4 ms.
CPU MT: 983.1 ms.
OpenCL: 5.7 ms, Process 4.9 ms (85.5%), Copy 0.8 ms (14.5%)
GLSL: 5.1 ms, Process -1.0 ms (-19.5%), Copy 6.1 ms (119.5%)
---------------------------------------------------------------
| GAUSSIAN BLUR |
---------------------------------------------------------------
CPU: 4601.4 ms.
CPU MT: 178.7 ms.
OpenCL: 9.2 ms, Process 8.5 ms (91.5%), Copy 0.8 ms (8.5%)
GLSL: 11.4 ms, Process -1.0 ms (-8.7%), Copy 12.4 ms (108.7%)
---------------------------------------------------------------
| SEPARABLE GAUSSIAN BLUR |
---------------------------------------------------------------
CPU: 838.0 ms.
CPU MT: 624.9 ms.
OpenCL: 1.8 ms, Process 1.1 ms (59.4%), Copy 0.7 ms (40.6%)
GLSL: 1.7 ms, Process -1.0 ms (-57.5%), Copy 2.7 ms (157.5%)
简单的事情 CPU MT 比 CPU 更慢; GLSL 传输比 OpenCL 更慢。(也有可能是程序没写好 [惭愧]-_-)
普通指令集 vs 增强指令集
- LERP
| CPU | 20.0 ms. | 9.4 ms. |
| CPU MT | 946.8 ms. | 660.6 ms. |
| OpenCL | 6.5 ms, Process 0.8 ms (12.0%), Copy 5.7 ms (88.0%) | 2.2 ms, Process 0.7 ms (31.1%), Copy 1.5 ms (68.9%) |
- BOX BLUR
| CPU | 1207.2 ms. | 1341.0 ms. |
| CPU MT | 619.2 ms. | 872.4 ms. |
| OpenCL | 5.9 ms, Process 5.0 ms (85.3%), Copy 0.9 ms (14.7%) | 5.6 ms, Process 4.8 ms (87.2%), Copy 0.7 ms (12.8%) |
- GAUSSIAN BLUR
| CPU | 1983.4 ms. | 3481.0 ms. |
| CPU MT | 96.4 ms. | 233.0 ms. |
| OpenCL | 9.4 ms, Process 8.6 ms (91.0%), Copy 0.8 ms (9.0%) | 9.4 ms, Process 8.6 ms (90.9%), Copy 0.9 ms (9.1%) |
- SEPARABLE GAUSSIAN BLUR
| CPU | 385.2 ms. | 813.4 ms. |
| CPU MT | 667.9 ms. | 773.2 ms. |
| OpenCL | 1.9 ms, Process 1.1 ms (59.2%), Copy 0.8 ms (40.8%) | 1.9 ms, Process 1.1 ms (56.7%), Copy 0.8 ms (43.3%) |
AMD APP Samples
AMD 的丰富的示例 Samples from the AMD APP SDK (with OpenCRun support)
AMD APP Samples
图片拷贝
__constant sampler_t imageSampler = CLK_NORMALIZED_COORDS_FALSE | CLK_ADDRESS_CLAMP | CLK_FILTER_NEAREST;
/* Copy input 2D image to output 2D image */
__kernel void image2dCopy(__read_only image2d_t input, __write_only image2d_t output)
{
int2 coord = (int2)(get_global_id(0), get_global_id(1));
uint4 temp = read_imageui(input, imageSampler, coord);
write_imageui(output, coord, temp);
}
/* Copy input 3D image to 2D image */
__kernel void image3dCopy(__read_only image3d_t input, __write_only image2d_t output)
{
int2 coord = (int2)(get_global_id(0), get_global_id(1));
/* Read first slice into lower half */
uint4 temp0 = read_imageui(input, imageSampler, (int4)(coord, 0, 0));
/* Read second slice into upper half */
uint4 temp1 = read_imageui(input, imageSampler, (int4)((int2)(get_global_id(0), get_global_id(1) - get_global_size(1)/2), 1, 0));
write_imageui(output, coord, temp0 + temp1);
}
sineWave
Simple kernel to modify vertex positions in sine wave pattern. param data data in global memory
__kernel
void sineWave(
__global float4 * pos,
unsigned int width,
unsigned int height,
float time)
{
unsigned int x = get_global_id(0);
unsigned int y = get_global_id(1);
// calculate uv coordinates
float u = x / (float) width;
float v = y / (float) height;
u = u*2.0f - 1.0f;
v = v*2.0f - 1.0f;
// calculate simple sine wave pattern
float freq = 4.0f;
float w = sin(u*freq + time) * cos(v*freq + time) * 0.5f;
// write output vertex
pos[y*width+x] = (float4)(u, w, v, 1.0f);
}
数据同步控制
#define GROUP_SIZE 64
__constant int mask[] =
{
1, -1, 2, -2
};
__kernel void MemoryModel(__global int *outputbuffer, __global int *inputbuffer)
{
__local int localBuffer[GROUP_SIZE];
__private int result=0;
__private size_t group_id=get_group_id(0);
__private size_t item_id=get_local_id(0);
__private size_t gid = get_global_id(0);
// Each workitem within a work group initialize one element of the local buffer
localBuffer[item_id]=inputbuffer[gid];
// Synchronize the local memory
barrier(CLK_LOCAL_MEM_FENCE);
// add 4 elements from the local buffer
// and store the result into a private variable
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
result += localBuffer[(item_id+i)%GROUP_SIZE];
}
// multiply the partial result with a value from the constant memory
result *= mask[group_id%4];
// store the result into a buffer
outputbuffer[gid]= result;
}
经典的流体模拟
FluidSimulation2D 搞 豹趣魔屏 的时候接触过,再次见到;作者说是 基于 OpenMP 版本改的。

OpenCL 主机与设备间数据传输
developer.amd.com/wordpress/media/2012/10/OpenCLTutorial-Chinese.pdf
读写传输命令、内存映射命令
RGB -> RGBA,就需要 clEnqueueCopyBufferToImage/clEnqueueCopyImageToBuffer:
- clEnqueueCopyBuffer: 缓存对象 —> 缓存对象
- clEnqueueCopyImage: 图像对象 —> 图像对象
- clEnqueueCopyBufferToImage: 缓存对象 —> 图像对象
- clEnqueueCopyImageToBuffer
- clEnqueueCopyBufferRect
操作对象数据
- 对象数据可以被拷贝到内存,从主机内存,或到其它对象
- 内存命令在命令缓冲区中排队,当命令被执行时处理
- clEnqueueReadBuffer(), clEnqueueReadImage()
- clEnqueueWriteBuffer(), clEnqueueWriteImage()
- clEnqueueCopyBuffer(), clEnqueueCopyImage()
- 数据可以在图像和缓冲区对象之间拷贝
- clEnqueueCopyImageToBuffer()
- clEnqueueCopyBufferToImage()
- 对象数据的区域可以被访问,通过映射进主机地址空间
- clEnqueueMapBuffer(), clEnqueueMapImage()
- clEnqueueUnmapMemObject()
OpenCL: C++ 实现双线性插值图像缩放
// 定义采样器
// CLK_NORMALIZED_COORDS_TRUE 指定使用归一化坐标
// CLK_ADDRESS_CLAMP 指定超出图像范围的颜色为黑色
// CLK_FILTER_LINEAR 指定使用双线性插值
__constant sampler_t sampler = CLK_NORMALIZED_COORDS_TRUE | CLK_ADDRESS_CLAMP | CLK_FILTER_LINEAR;
__kernel void image_scaling(__read_only image2d_t sourceImage,
__write_only image2d_t destinationImage,
const float widthNormalizationFactor,
const float heightNormalizationFactor)
{
// 从 glob_id 中获取目标像素坐标
int2 coordinate = (int2)(get_global_id(0), get_global_id(1));
// 计算归一化浮点坐标
float2 normalizedCoordinate = convert_float2(coordinate) * (float2)(widthNormalizationFactor, heightNormalizationFactor);
// 根据归一化坐标从原图中读取像素数据
float4 colour = read_imagef(sourceImage, sampler, normalizedCoordinate);
// 将像素数据写入目标图像
write_imagef(destinationImage, coordinate, colour);
}
零拷贝
CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR Vs CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR Vs CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR
使用 map 代替 copy 假设 OpenCL 应用程序对数据流有完全的控制,即目标和源内存对象的创建都由 OpenCL 应用程序管理。这是最简单的情况,可以通过以下步骤避免内存复制: CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR 是避免在这种情况下复制数据的唯一方法。 对于其他标志,如 CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR 或 CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,驱动程序必须做额外的内存复制以便 GPU 访问。
OpenCL memory object 之 传输优化
如果 device 及操作系统支持 zero copy,则下面 buffer 类型可以使用:
- The CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR buffer OpenCL 的底层实施可能使用页锁定内存。 – zero copy buffer 驻留在 host。 – host 能够以全带宽访问它。 – device 通过 interconnect bandwidth 访问它。 – 这块 buffer 被分配在 prepinned 的 host memory 中。
- The CL_MEM_USE_PERSISTENT_MEM_AMD buffer is – zero copy buffer 驻留在 GPU device 中。 – GPU 能全带宽访问它。 – host 能够以 interconnect 带宽访问它(例如 streamed 写带宽 host->device,低的读带宽,因为没有 cache 利用)。 – 在 host 和 device 之间通过 interconnect 带宽传输数据。
注意:创建 buffer 的大小是平台 dependience 的,比如在某个平台上一个 buffer 不能超过 64M,总的 buffer 不能超过 128M 等。
- buffer = clCreateBuffer(CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR | CL_MEM_READ_ONLY)
- address = clMapBuffer( buffer )
- memset( address ) or memcpy( address ) (if possible, using multiple CPU cores)
- clEnqueueUnmapMemObject( buffer )
- clEnqueueNDRangeKernel( buffer )
内存问题探讨
CL_MEM_USE_PERSISTENT_MEM_AMD cl_khr_egl_image
- CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR:直接使用 host 上一段已经分配的 mem 供 device 使用。
- 在 GPU 上,CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR 很可能会分配所谓的页锁定或固定内存。这种内存对于主机 -> GPU 内存传输速度最快,这是推荐的复制方式。
- 当它指明时,OpenCL 的实现将使用由 host_ptr 指向的内存来作为 cl_mem 对象的存储,将 host_ptr 指向的内容缓冲(cache)到对应的设备上,在 kernel 执行的过程中就可以使用这些内容。
- CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR maintains a reference to that memory area and depending on the implementation it might access it directly while kernels are executing or it might cache it. You must use mapbuffer to provide synchronization points if you want to write cross platform code using this.
- CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR:在 host 上新开辟一段内存供 device 使用。
- 只在主机上分配内存,根本不会发生任何转移:这就像做一个 malloc 而不是填充内存。
- 个选项要求 OpenCL 在主程序可以访问的存储位置来放置 buffer。
- CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR is the only one that is often pinned memory. As an example on AMD this one allocates a pinned memory area. Often if you use CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR it will simply memcpy internally to a pinned memory area and use that. By using ALLOC_HOST_PTR you will avoid that. But yet again this depends on the implementation and you must read the manufacturers documentation on if this will provide you with pinned memory or not.
- CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR:在 device 上开辟一段内存供 device 使用,并赋值为 host 上一段已经存在的 mem。
- 将在设备上分配一个缓冲区,很可能是 GPU 上的 RAM,然后将整个主机缓冲区复制到设备内存中。
- 它要求 OpenCL 为存储对象分配空间并复制(copy)host_ptr 指向的内容到相应的存储中。
- 在使用时可以这么用,如果使用有独立显存的 GPU,使用 CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR 可以在主存中 malloc 一段空间,再使用它来创建,并初始化 cl_men 对象,创建完毕后,即可将这段空间 free,那么使用 COPY 可以节约主存,而利用显存。
- 经过实际测试,貌似 mapbuf 后内存又会涨回来(NVIDIA Corporation),靠……。
- CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR simply copies the values at a time of creation of the buffer.
Arm Mali 内存文档
这个文档讲的最清楚。 Arm Mali Bifrost OpenCL Developer Guide Version 1.0 About memory allocation
- CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR
- This is a hint to the driver indicating that the buffer is accessed on the host side. To use the buffer on the application processor side, you must map this buffer and write the data into it. This is the only method that does not involve copying data. If you must fill in an image that is processed by the GPU, this is the best way to avoid a copy.
- CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR
- Copies the data pointed to by the
host_ptrargument into memory allocated by the driver.
- Copies the data pointed to by the
- CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR
- Copies the data pointed to by the host memory pointer into the buffer when the first kernel using this buffer starts running. This flag enforces memory restrictions that can reduce performance. Avoid using this if possible.
- When a map is executed, the memory must be copied back to the provided host pointer. This significantly increases the cost of map operations.
Arm recommends the following:
- Do not use private or local memory to improve memory read performance.
- If your kernel is memory bandwidth bound, try using a simple formula to compute variables instead of reading from memory. This saves memory bandwidth and might be faster.
- If your kernel is compute bound, try reading from memory instead of computing variables. This saves computations and might be faster.
Use CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR to avoid copying memory

Memory buffer created by clCreateBuffer(CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR)
Do not create buffers with CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR if possible

Memory buffer created by clCreateBuffer(CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR)
Do not allocate memory buffers created with malloc() for OpenCL applications

Memory buffer created by malloc()
You must allocate the memory in OpenCL with CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR because it ensures that the memory pages are always mapped into physical memory.
- Optimizing OpenCL for Mali GPUs
- Do not use clFinish() for synchronization
- Instead, where possible, use clWaitForEvents() or callbacks to ensure that the control thread and OpenCL can work in parallel.
- Do not use any of the clEnqueueMap() operations with a blocking call
- Use clWaitForEvents() or callbacks to ensure that the control thread and OpenCL can work in parallel.
- Do not use clFinish() for synchronization
- OpenCL Optimizations List
自己测试结果。
集成显卡的情况:
- CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR – 会新申请内存。
- CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR – 这个也会新申请内存。奇怪?
- CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR – 这个也会新申请内存。
集成显卡,上传 alloc,临时 alloc,下载 usehost:
create 0.0024 ms. upload 0.0088 ms. scale= 0.0577 ms. download 0.0001 ms.
全部 alloc 的情况:
create 0.0047 ms. upload 0.0085 ms. scale= 0.0576 ms. download 0.0078 ms.
// Debug 1.2
create 0 ms. upload 13 ms. scale 0 ms. download 73 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 12 ms. scale 0 ms. download 27 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 9 ms. scale 0 ms. download 22 ms.
create 1.3333 ms. upload 11.3333 ms. scale 0.0000 ms. download 40.6667 ms.
// Debug 3.0
create 1 ms. upload 16 ms. scale 13 ms. download 7 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 9 ms. scale 11 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1 ms. upload 10 ms. scale 10 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1.3333 ms. upload 11.6667 ms. scale 11.3333 ms. download 5.0000 ms.
// Debug 2.0
create 0 ms. upload 13 ms. scale 12 ms. download 5 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 10 ms. scale 10 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1 ms. upload 10 ms. scale 10 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1.0000 ms. upload 11.0000 ms. scale 10.6667 ms. download 4.3333 ms.
Notes
- C++ Wrapper for OpenCL : www.khronos.org/registry/cl/specs/opencl-cplusplus-1.2.pdf
- OpenCL Reference : www.khronos.org/registry/cl/sdk/1.2/docs/man/xhtml/
- Quick reference card : www.khronos.org/registry/cl/sdk/1.2/docs/OpenCL-1.2-refcard.pdf
- Complete OpenCL tutorial : www.cmsoft.com.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&layout=blog&id=41&Itemid=75
OpenCL https://man.opencl.org/
Debug\binaries.exe
This sample intends to demonstrate how to use separate compilation and consumption of OpenCL program by saving and loading program binaries.
该示例旨在通过 保存 和 加载 程序二进制文件来演示如何使用 OpenCL 程序的单独 编译 和 使用 。
Debug\blur.exe
This sample intends to demonstrate how to use different techniques of data exchange between workitems in workgroup, query various extensions applicable and use compile options to touch up kernel sources at runtime to produce the best kernel implementation for the task.
该示例旨在演示如何在工作组中的工作项之间使用 不同的数据交换技术 , 查询各种适用的扩展并使用编译选项在 运行时修改内核源代码 ,从而为任务生成最佳内核实现。
Debug\copybuffer.exe
In this very simple sample, OpenCL APIs are used to copy the contents of one buffer to another buffer on the OpenCL device. To do this, OpenCL APIs are used to create both buffers, to create the OpenCL command queue, and to initialize the source buffer and verify the contents of the destination buffer on the host. By default, this sample will run in the first enumerated OpenCL device on the first enumerated OpenCL platform. To run on a different OpenCL device or platform, please use the provided command line options.
在这个非常简单的示例中,OpenCL API 用于将一个缓冲区的 内容复制 到 OpenCL 设备上的另一个缓冲区。 为此,OpenCL API 用于创建两个缓冲区、创建 OpenCL 命令队列、初始化源缓冲区并验证主机上目标缓冲区的内容。 默认情况下,此示例将在第一个枚举 OpenCL 平台上的第一个枚举 OpenCL 设备中运行。 要在不同的 OpenCL 设备或平台上运行,请使用提供的命令行选项。
Debug\copybufferkernel.exe
This example uses an OpenCL kernel to do work. An OpenCL kernel is a short program defining what one OpenCL work item should do. In this case, each OpenCL work item will copy one value from a source buffer to a destination buffer. Since this sample launches one work item for every element in the source buffer, behaviorally this sample will do exactly the same thing as the copy buffer sample. In this sample, the source code for the OpenCL kernel is embedded into the host code as a raw string. At runtime, an OpenCL program is created from the raw string, and the OpenCL device compiler is invoked to compile the OpenCL program for the OpenCL device. This isn't the only way to create OpenCL programs, but it is fairly common, especially while learning and developing an OpenCL application. By default, this sample will run in the first enumerated OpenCL device on the first enumerated OpenCL platform. To run on a different OpenCL device or platform, please use the provided command line options.
此示例使用 OpenCL 内核来完成工作。 OpenCL 内核是一个简短的程序,它定义了一个 OpenCL 工作项应该做什么。 在这种情况下,每个 OpenCL 工作项会将一个值从源缓冲区复制到目标缓冲区。 由于此示例为源缓冲区中的每个元素启动一个工作项,因此从行为上讲,此示例将执行与复制缓冲区示例完全相同的操作。 在此示例中,OpenCL 内核的源代码作为原始字符串嵌入到主机代码中。 在运行时,从原始字符串创建 OpenCL 程序,并调用 OpenCL 设备编译器为 OpenCL 设备编译 OpenCL 程序。 这不是创建 OpenCL 程序的唯一方法,但它相当普遍,尤其是在学习和开发 OpenCL 应用程序时。 默认情况下,此示例将在第一个枚举 OpenCL 平台上的第一个枚举 OpenCL 设备中运行。 要在不同的 OpenCL 设备或平台上运行,请使用提供的命令行选项。
Debug\enumopencl.exe
This is a very simple sample that demonstrates how to enumerate the OpenCL platforms that are installed on a machine, and the OpenCL devices that these platforms expose. This is one of the few samples that uses the OpenCL C APIs, as described in the OpenCL specification. Most of the other samples use the OpenCL C++ API bindings, since they make it a lot easier to write and understand OpenCL code! This is a good first sample to run to verify that OpenCL is correctly installed on your machine, and that your build environment is correctly setup.
这是一个非常简单的示例,演示了如何枚举安装在机器上的 OpenCL 平台,以及这些平台公开的 OpenCL 设备。 这是使用 OpenCL C API 的少数示例之一,如 OpenCL 规范中所述。 大多数其他示例都使用 OpenCL C++ API 绑定,因为它们使编写和理解 OpenCL 代码变得更加容易! 这是一个很好的第一个示例,可以运行以验证 OpenCL 是否正确安装在您的机器上,以及您的构建环境是否正确设置。
Debug\reduce.exe & reducecpp.exe
This sample intends to demonstrate how to query various extensions applicable in the context of a reduction algorithm, touch up kernel sources at runtime to select the best kernel implementation for the task.
此示例旨在演示如何查询适用于缩减算法的各种扩展,在运行时修改内核源以选择任务的最佳内核实现。
Debug\saxpy.exe & saxpycpp.exe
This sample intends to be a minimal end-to-end OpenCL application doing actual device-side computation. The structure of the sample rhymes well with the How Does OpenCL Work? chapter of the OpenCL-Guide, particularly the Executing an OpenCL Program part. This sample is implemented using both C and C++ languages to demonstrate the difference in verbosity when using the naked C bindings compared to the C++ wrapper.
此示例旨在成为执行实际设备端计算的最小端到端 OpenCL 应用程序。示例的结构与 OpenCL 如何工作? OpenCL 指南的章节,特别是执行 OpenCL 程序部分。 此示例是使用 C 和 C++ 语言实现的,以展示使用裸 C 绑定与 C++ 包装器相比在详细程度方面的差异。
- 举例
- 顶点(Vertex)和图像数据由 OpenCL 的生成,然后用 OpenGL 渲染
- 图像由 OpenGL 渲染后,由 OpenCL 内核后处理
Debug\conwaycpp.exe 扩展
This sample intends to demonstrate how to share images (textures) between OpenCL and OpenGL. How Does OpenCL-OpenGL Interop? chapter of the OpenCL-Guide lays out the fundamentals of OpenCL-OpenGL interoperability.
此示例旨在演示如何在 OpenCL 和 OpenGL 之间共享图像(纹理)。 OpenCL-OpenGL 如何互操作? OpenCL 指南的第 1 章阐述了 OpenCL-OpenGL 互操作性的基础知识。
Debug\histogramcpp.exe 扩展
The sample calculate the histogram of a random sequence with global atomic add and when it is possible, it's using local atomic add.
This sample intends to be a minimal end-to-end OpenCL application doing actual device-side computation. The structure of the sample rhymes well with the How Does OpenCL Work? chapter of the OpenCL-Guide, particularly the Executing an OpenCL Program part. This sample is implemented using C++ languages.
该示例使用全局原子添加计算随机序列的直方图,并且在可能的情况下,它使用局部原子添加。
此示例旨在成为执行实际设备端计算的最小端到端 OpenCL 应用程序。示例的结构与 OpenCL 如何工作? OpenCL 指南的章节,特别是执行 OpenCL 程序部分。 此示例使用 C++ 语言实现。
Debug\nbodycpp.exe 扩展
This sample intends to demonstrate how to share (vertex) buffers between OpenCL and OpenGL. How Does OpenCL-OpenGL Interop? chapter of the OpenCL-Guide lays out the fundamentals of OpenCL-OpenGL interoperability.
此示例旨在演示如何在 OpenCL 和 OpenGL 之间共享(顶点)缓冲区。 OpenCL-OpenGL 如何互操作? OpenCL 指南的第 1 章阐述了 OpenCL-OpenGL 互操作性的基础知识。
Debug\cargstest.exe
A simple argument parser library
https://github.com/likle/cargs.git
OpenCL-CLHPP
- Debug\headerexample.exe OpenCL-CLHPP
- Debug\trivial.exe OpenCL-CLHPP
- Debug\trivialSizeTCompat.exe OpenCL-CLHPP
http://khronosgroup.github.io/OpenCL-CLHPP/
对于许多大型应用程序,C++ 是首选语言,因此为 OpenCL 定义 C++ 绑定似乎是合理的。
该接口包含在单个 C++ 头文件 opencl.hpp 中,所有定义都包含在命名空间 cl 中。不需要包含 cl.h 并使用 C++ 或原始 C 绑定;只需包含 opencl.hpp 就足够了。
绑定本身是轻量级的,并且与底层 C API 密切对应。使用 C++ 绑定不会引入额外的执行开销。
新标头中有许多兼容性、可移植性和内存管理修复以及其他 OpenCL 2.0 功能。因此,标头不能直接向后兼容,因此我们将其作为 opencl.hpp 而不是新版本的 cl.hpp 发布。
OpenCLUtils.lib & OpenCLUtilsCpp.lib
OpenCL SDK 中有两个库,所有示例都在不同程度上使用它们。一个这样的库是 OpenCL 实用程序库,它是一个导出库,旨在简化 OpenCL 的使用,而 OpenCL SDK 库构建在它之上,但在安装 SDK 时不会导出。 OpenCL SDK 库以在 SDK 示例上下文之外可能没有意义的方式扩展了实用程序库。
One may think of this library as analogous to GLU and GLUT in the domain of OpenGL. A set of utilities which condense common tasks into singular functions or add missing functionality of the API which otherwise couldn't be added as a non-API-breaking change. For a complete list utilities provided by this library, refer to the OpenCL Utility Library docs.
The OpenCL Utility Library provides both C and C++ bindings with near feature parity. The utilities are broken into to libraries, OpenCLUtils and OpenCLUtilsCpp. To include them in your project, include <CL/Utils/Utils.h>/<CL/Utils/Utils.hpp> and link to their libraries respectively.
OpenCL 实用程序库提供具有接近功能奇偶性的 C 和 C++ 绑定。这些实用程序分为库、OpenCLUtils 和 OpenCLUtilsCpp。 要将它们包含在您的项目中,请包含 <CL/Utils/Utils.h>/<CL/Utils/Utils.hpp> 并分别链接到它们的库。
OpenCLSDK.lib & OpenCLSDKCpp.lib
The SDK library extends the Utility library by deduplicating common tasks like command-line argument parsing, selecting devices, logging, and other contentious tasks which your application likely does differently, hence the value in shipping it for external use, moreover promise forward and/or backward compatibility is low. For a complete list functionality provided by this library, refer to the OpenCL SDK Library docs.
The OpenCL SDK Library hosts both C and C++ utilities which are generally useful for writing OpenCL applications but are either dependency-heavy or contentious. Because these utilities aren't the subject of universal interest, these utilities are not exported, meaning SDK installations won't install their headers nor their libraries. Doing so the OpenCL Utility Library can be kept dependency-free. The utilities are broken into to libraries, OpenCLSDK and OpenCLSDKCpp. Samples include <CL/Utils/Utils.h>/<CL/Utils/Utils.hpp> and link to their libraries respectively.
OpenCL SDK 库包含 C 和 C++ 实用程序,这些实用程序通常对编写 OpenCL 应用程序很有用,但依赖关系严重或有争议。 因为这些实用程序不是普遍感兴趣的主题,所以不会导出这些实用程序,这意味着 SDK 安装不会安装它们的头文件或库。这样做可以使 OpenCL 实用程序库保持无依赖关系。 这些实用程序分为库、OpenCLSDK 和 OpenCLSDKCpp。示例包括 <CL/Utils/Utils.h>/<CL/Utils/Utils.hpp> 并分别链接到它们的库。
骚操作
选择显卡 vendor
我电脑存在多个 GPU,优先 英伟达、AMD、Intel,其它就无所谓了。 https://pci-ids.ucw.cz/ 完整表格:https://pci-ids.ucw.cz/v2.2/pci.ids
#define OPENCL_VENDOR_NVIDIA 4318 // 0x10de NVIDIA Corporation
#define OPENCL_VENDOR_AMD1 4098 // 0x1002 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI]
#define OPENCL_VENDOR_AMD2 4130 // 0x1022 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD]
#define OPENCL_VENDOR_INTEL 32902 // 0x8086 Intel Corporation
#define OPENCL_VENDOR_VMWARE 0x15ad // 0x15ad VMware
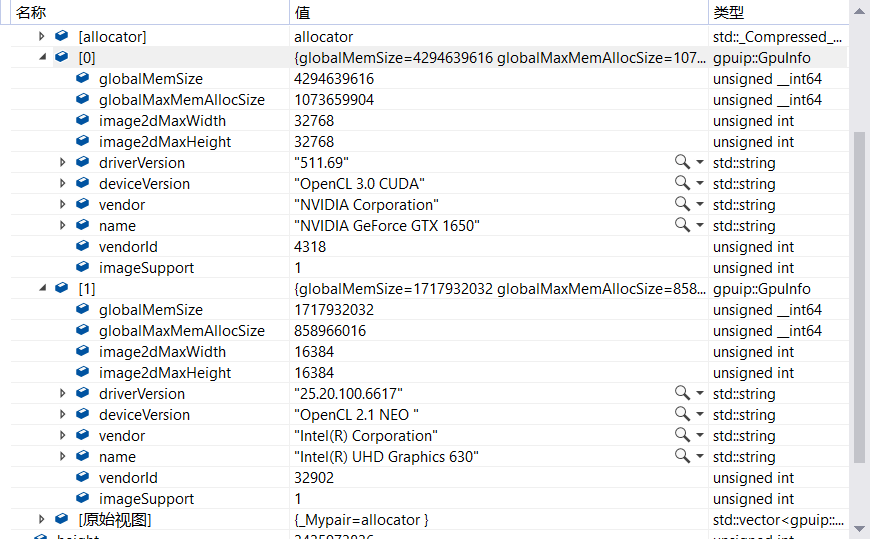
我 DELL 游戏本的参数
游戏本独立显卡:
NVIDIA Corporation
preload 32 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 153 ms. scale 1 ms. download 89 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 143 ms. scale 1 ms. download 102 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 152 ms. scale 0 ms. download 87 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 157 ms. scale 1 ms. download 72 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 219 ms. scale 4 ms. download 195 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 209 ms. scale 3 ms. download 90 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 196 ms. scale 5 ms. download 104 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 225 ms. scale 14 ms. download 123 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 153 ms. scale 2 ms. download 114 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 230 ms. scale 4 ms. download 141 ms.
create 0.0000 ms. upload 183.7000 ms. scale 3.5000 ms. download 111.7000 ms.
NVIDIA Corporation
preload 12 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 181 ms. scale 1 ms. download 108 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 136 ms. scale 0 ms. download 70 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 127 ms. scale 1 ms. download 70 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 164 ms. scale 3 ms. download 91 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 191 ms. scale 3 ms. download 88 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 190 ms. scale 4 ms. download 101 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 187 ms. scale 3 ms. download 103 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 192 ms. scale 3 ms. download 94 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 210 ms. scale 3 ms. download 93 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 185 ms. scale 3 ms. download 94 ms.
create 0.0000 ms. upload 176.3000 ms. scale 2.4000 ms. download 91.2000 ms.
游戏本集成显卡:
Intel(R) Corporation
preload 1301 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 107 ms. scale 6 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 18 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 18 ms. scale 6 ms. download 3 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 16 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 16 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1 ms. upload 17 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1 ms. upload 16 ms. scale 6 ms. download 3 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 16 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 20 ms. scale 5 ms. download 7 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 17 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1.6000 ms. upload 26.1000 ms. scale 5.3000 ms. download 4.1000 ms.
Intel(R) Corporation
preload 2 ms.
create 0 ms. upload 182 ms. scale 17 ms. download 6 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 17 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 17 ms. scale 5 ms. download 3 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 16 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 19 ms. scale 6 ms. download 3 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 18 ms. scale 6 ms. download 3 ms.
create 3 ms. upload 21 ms. scale 5 ms. download 5 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 18 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 2 ms. upload 20 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1 ms. upload 18 ms. scale 5 ms. download 4 ms.
create 1.8000 ms. upload 34.6000 ms. scale 6.4000 ms. download 4.0000 ms.
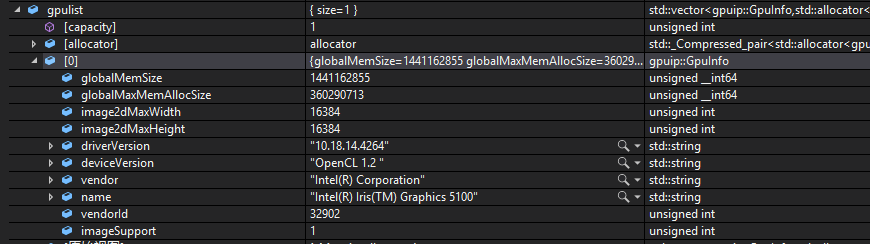
我 Mac Mini 参数
多显卡调度能力
它的 API 是基于多个显卡设计的,可以多显卡调度。
https://developer.nvidia.com/opencl
OpenCL Simple Multi-GPU
This application demonstrates how to make use of multiple GPUs in OpenCL.
What is the best way to programmatically choose the best GPU in OpenCL?
感觉最靠谱的还是,写个程序都跑一下,看哪个 gpu 更快。
OpenCL Crash
- opencl.dll_3.0.1.0_12ec_fastapp.exe_2022.5.12.2187_4f6a26c.txt
- 516: ExceptionCode: c0000094 (Integer divide-by-zero)
EXCEPTION_RECORD: (.exr -1) ExceptionAddress: 62bd3fbc (igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0x000e982c) ExceptionCode: c0000094 (Integer divide-by-zero) ExceptionFlags: 00000000 NumberParameters: 0 STACK_TEXT: 0efaee9c 62bd3fbc igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0xe982c 0efaeea4 62c450c3 igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0x5cd73 0efaeebc 62bf61a8 igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xde58 0efaeed8 62af7337 igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0xcba7 0efaef14 62bf7c08 igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xf8b8 0efaef44 62bf7fe7 igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xfc97 0efaef94 62b0055b igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0x15dcb 0efaeff8 62bf708e igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xed3e 0efaf044 62bf6f9b igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xec4b 0efaf080 62bf6cc6 igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xe976 0efaf0b8 62c03937 igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0x1b5e7 0efaf0e8 62b0c425 igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0x21c95 0efaf110 62b0c303 igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0x21b73 0efaf124 62b0c1e8 igdrcl32_62ac0000!GTPin_Init+0x21a58 0efaf180 62acd09b igdrcl32_62ac0000!clGetPlatformIDs+0x20b 0efaf2a4 62adfc8f igdrcl32_62ac0000!clEnqueueTask+0x29f 0efaf2c0 693912ec opencl+0x12ec 0efaf2f4 693965a7 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x5b7 0efaf734 7734a234 ntdll+0x5a234 0efaf758 76f6bd07 KERNELBASE+0x11bd07 0efaf770 69396634 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x644 - opencl.dll_3.0.1.0_12ec_fastapp.exe_2022.5.12.2187_b3fb447.txt
- 519: ExceptionCode: c0000094 (Integer divide-by-zero)
EXCEPTION_RECORD: (.exr -1) ExceptionAddress: 6abb3fbc (igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0x000e982c) ExceptionCode: c0000094 (Integer divide-by-zero) ExceptionFlags: 00000000 NumberParameters: 0 STACK_TEXT: 0f0beb1c 6abb3fbc igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0xe982c 0f0beb24 6ac250c3 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0x5cd73 0f0beb3c 6abd61a8 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xde58 0f0beb58 6aad7337 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0xcba7 0f0beb94 6abd7c08 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xf8b8 0f0bebc4 6abd7fe7 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xfc97 0f0bec14 6aae055b igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0x15dcb 0f0bec78 6abd708e igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xed3e 0f0becc4 6abd6f9b igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xec4b 0f0bed00 6abd6cc6 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0xe976 0f0bed38 6abe3937 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetGLContextInfoKHR+0x1b5e7 0f0bed68 6aaec425 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0x21c95 0f0bed90 6aaec303 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0x21b73 0f0beda4 6aaec1e8 igdrcl32_6aaa0000!GTPin_Init+0x21a58 0f0bee00 6aaad09b igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clGetPlatformIDs+0x20b 0f0bef24 6aabfc8f igdrcl32_6aaa0000!clEnqueueTask+0x29f 0f0bef40 6e8d12ec opencl+0x12ec 0f0bef74 6e8d65a7 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x5b7 0f0bf3b4 77187ec4 ntdll+0x57ec4 0f0bf3d8 76c44137 KERNELBASE+0x114137 0f0bf3f0 6e8d6634 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x644 - opencl.dll_3.0.1.0_132c_fastapp.exe_2022.5.12.2187_5b1e195.txt
- 513: ExceptionCode: c0000094 (Integer divide-by-zero)
EXCEPTION_RECORD: (.exr -1) ExceptionAddress: 0f64811c (igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x0008811c) ExceptionCode: c0000094 (Integer divide-by-zero) ExceptionFlags: 00000000 NumberParameters: 0 STACK_TEXT: 09feee6c 0f64811c igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x8811c 09feee74 0f7972b9 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x1d72b9 09feee8c 0f731288 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x171288 09feeea8 0f601d64 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x41d64 09feeee4 0f733e97 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x173e97 09feef14 0f734180 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x174180 09feef64 0f60a121 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x4a121 09feefc8 0f623464 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x63464 09fef014 0f62338b igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x6338b 09fef050 0f6230c9 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x630c9 09fef088 0f76e5ec igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x1ae5ec 09fef0c0 0f644938 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x84938 09fef11c 0f5d5784 igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x15784 09fef1f4 0f5e7b3f igdrcl32_f5c0000+0x27b3f 09fef210 719c132c opencl+0x132c 09fef244 719c65a7 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x5b7 09fef684 77199dd6 ntdll+0x59dd6 09fef6a8 76eae917 KERNELBASE+0x10e917 09fef6c0 719c6634 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x644 - opencl.dll_3.0.1.0_5260_fastapp.exe_2022.5.12.2187_985f245.txt
- 482: ExceptionCode: c0000005 (Access violation)
EXCEPTION_RECORD: (.exr -1) ExceptionAddress: 71f05260 (opencl!clGetDeviceIDs+0x00000040) ExceptionCode: c0000005 (Access violation) ExceptionFlags: 00000000 NumberParameters: 2 Parameter[0]: 00000000 Parameter[1]: 5d45c448 Attempt to read from address 5d45c448 STACK_TEXT: 09abf588 71f05260 opencl!clGetDeviceIDs+0x40 - opencl.dll_3.0.1.0_8112_fastapp.exe_2022.5.12.2187_3e76613.txt win7_64
- 484: ExceptionCode: c0000005 (Access violation)
EXCEPTION_RECORD: (.exr -1) ExceptionAddress: 6da28112 (opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x00002122) ExceptionCode: c0000005 (Access violation) ExceptionFlags: 00000000 NumberParameters: 2 Parameter[0]: 00000000 Parameter[1]: 00000000 Attempt to read from address 00000000 STACK_TEXT: 0fbfeea8 6da28112 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x2122 0fbff180 6da26210 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x220 0fbff5c4 776fbdf4 ntdll+0x3bdf4 0fbff5e0 76d2d69e kernel32+0x2d69e 0fbff5f8 6da26634 opencl!clWaitForEvents+0x644
参考资料快照
- https://blog.csdn.net/l12212/article/details/117251631
- https://blog.csdn.net/cutemypig/article/details/122419925
- https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneTBB
- https://www.khronos.org/opencl/
- https://community.amd.com/t5/archives-discussions/what-s-faster-clenqueuereadbuffer-clenqueuemapbuffer/m-p/132962
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/441366127
- https://gist.github.com/tomoaki0705/bee46d7a35fa220459c1c76b243759bb
- https://0cch.com/2022/03/08/oneapi-summary/
- https://www.cnblogs.com/yssongest/p/5303151.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/archive/2011/11/12/2246808.html
- https://www.bookstack.cn/read/Heterogeneous-Computing-with-OpenCL-2.0/content-chapter2-2.2-chinese.md
- https://www.mql5.com/zh/articles/405
- https://www.mql5.com/zh/articles/407
- https://github.com/OpenCL/AMD_APP_samples
- https://www.cnblogs.com/feihu-h/p/12084536.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/10km/article/details/50755584
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/25496656/cl-mem-use-host-ptr-vs-cl-mem-copy-host-ptr-vs-cl-mem-alloc-host-ptr
- https://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/archive/2011/12/18/2291741.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/u012507022/article/details/106874650/
- https://man.opencl.org/clCreateBuffer.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38498942/article/details/117063298
- https://blog.csdn.net/hanxing0/article/details/32344099
- https://blog.csdn.net/breakawayroad/article/details/9003632
- https://developer.arm.com/documentation/101574/0100/optimizing-opencl-for-mali-gpus/optimizing-memory-allocation/about-memory-allocation
- https://developer.arm.com/documentation/101574/0100/optimizing-opencl-for-mali-gpus
- https://developer.arm.com/documentation/101574/0100/opencl-optimizations-list
- https://developer.arm.com/documentation/101574/0100/opencl-optimizations-list/general-optimizations
- https://man.opencl.org/
- https://github.com/likle/cargs.git
- http://khronosgroup.github.io/OpenCL-CLHPP/
- https://pci-ids.ucw.cz/
- https://developer.nvidia.com/opencl
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33333468/what-is-the-best-way-to-programmatically-choose-the-best-gpu-in-opencl
- 编程与调试 C++ -- OpenCL 2.0 异构计算 笔记 | 28 Apr 2022
- 编程与调试 C++ -- OpenCL & CUDA 初探 | 16 Apr 2022
 .
.