图形学笔记 -- OpenGL 毕业报告 / 3D 水母程序 Jellyfish
蒙皮骨骼动画  不依赖任何 3D 引擎,全部采用原生 OpenGL API 实现。包含:1. 渲染,2. 骨骼动画,3. 物理模拟。程序下载:
Jellyfish.zip
不依赖任何 3D 引擎,全部采用原生 OpenGL API 实现。包含:1. 渲染,2. 骨骼动画,3. 物理模拟。程序下载:
Jellyfish.zip
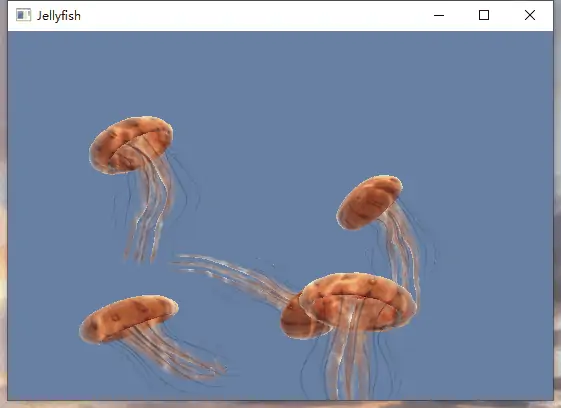
先上效果
数学基础函数
M4x4 采用行优先的内存结构,glm::mat4 是 列优先记法。
// 计算投影视锥体
GLfloat* M4x4_makeFrustum(GLfloat left, GLfloat right,
GLfloat bottom, GLfloat top,
GLfloat znear, GLfloat zfar, GLfloat* r);
// 转置矩阵
GLfloat* M4x4_transpose(GLfloat* m, GLfloat* r);
// 计算标准正交矩阵的逆矩阵 4x4
GLfloat* M4x4_inverseOrthonormal(GLfloat* m, GLfloat* r);
// 矩阵相乘
GLfloat* M4x4_mul(GLfloat* a, GLfloat* b, GLfloat* r);
// 计算 透视投影
GLfloat* M4x4_makePerspective(GLfloat fovy, GLfloat aspect, GLfloat znear, GLfloat zfar, GLfloat* r);
// 平移矩阵
GLfloat* M4x4_makeTranslate3(GLfloat x, GLfloat y, GLfloat z, GLfloat* r);
// 矩阵平移
GLfloat* M4x4_translate3(GLfloat x, GLfloat y, GLfloat z, GLfloat* m, GLfloat* r);
// 矩阵旋转
GLfloat* M4x4_rotate(GLfloat angle, glm::vec3 axis, GLfloat* m, GLfloat* r);
// 定义一个视图矩阵
GLfloat* M4x4_makeLookAt(glm::vec3 eye, glm::vec3 center, glm::vec3 up, GLfloat* r);
// 平移矩阵
GLfloat* M4x4_makeTranslate(glm::vec3 v, GLfloat* r);
// 矩阵缩放
GLfloat* M4x4_scale1(GLfloat k, GLfloat* m, GLfloat* r);
// 向量点乘
GLfloat V3_dot(glm::vec3 a, glm::vec3 b);
// 向量叉乘
glm::vec3 V3_cross(glm::vec3 a, glm::vec3 b);
// 向量加法
glm::vec3 V3_add(glm::vec3 a, glm::vec3 b, glm::vec3& r);
// 向量缩放
glm::vec3 V3_scale(glm::vec3 a, GLfloat k);
// 向量方向:向量 A 到向量 B 的方向(标准化)
glm::vec3 V3_direction(glm::vec3 a, glm::vec3 b);
// 向量减法
glm::vec3 V3_sub(glm::vec3 a, glm::vec3 b);
// 向量长度
GLfloat V3_length(glm::vec3 a);
// 向量标准化
glm::vec3 V3_normalize(glm::vec3 a);
// 向量取反
glm::vec3 V3_neg(glm::vec3 a);
模型顶点数据
struct AttrNode {
glm::vec3 aVertexPosition;
glm::vec3 aVertexNormal;
glm::vec3 aVertexColor;
glm::vec3 aTextureCoord;
glm::vec4 aSkinWeight;
};
struct ShaderProgram {
GLuint program;
GLint vertexPositionAttribute;
GLint vertexNormalAttribute;
GLint vertexColorAttribute;
GLint textureCoordAttribute;
GLint skinWeightAttribute;
GLint world;
GLint worldView;
GLint worldViewProj;
GLint view;
GLint viewInv;
GLint sampler[3];
GLint joint[JOINT_COUNT]; // 关节
GLint joint0InvTranspose;
GLint currentTime;
GLint currentJellyfishTime;
};
struct ShaderProgramData {
GLfloat mWorld[16];
GLfloat mView[16];
GLfloat mProjection[16];
GLfloat mWorldView[16];
GLfloat mWorldViewProj[16];
GLfloat mViewInv[16];
// GLfloat* mTemp;
GLfloat joint[JOINT_COUNT][16];
GLfloat joint0InvTranspose[16];
// GLfloat uCurrentJellyfishTime;
};
骨骼动画原理
骨骼动画与蒙皮矩阵
建立 1 个控制点 和 4 个骨骼节点:

aSkinWeight 可以根据 y 坐标简单算出来:
int weightSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vertexPositions.size(); i = i + 3) {
GLfloat value = vertexPositions[i + 1]; // y
GLfloat ypos = -value / 3;
GLfloat w0 = max(min(-ypos + 1, 1), 0);
GLfloat w1 = max(min(ypos, -ypos + 2), 0);
GLfloat w2 = max(min(ypos - 1, -ypos + 3), 0);
GLfloat w3 = max(min(ypos - 2, 1), 0);
weightData[weightSize++] = w0;
weightData[weightSize++] = w1;
weightData[weightSize++] = w2;
weightData[weightSize++] = w3;
}
对应的权重图,权重分布:

JellyfishTarget
struct JellyfishTarget {
glm::vec3 pos;
GLfloat scale; // 缩放
GLfloat id;
GLfloat time;
GLfloat speed;
JellyfishTarget(GLfloat tx, GLfloat ty, GLfloat tz, GLfloat scale, GLfloat id) {
this->pos = glm::vec3(tx, ty, tz);
this->scale = scale;
this->id = id;
this->time = (rand() % 1000 * 1.0 / 1000) * 100;
this->speed = (rand() % 1000 * 1.0 / 1000) + 0.5;
}
};
关节 Spring3D
struct Spring3D {
glm::vec3 pos; // 在父关节中的坐标
GLfloat gravity = -0.005; // 向下的重力
GLfloat spring = 2; // 弹性
GLfloat lookat[16]; // 相对父关节朝向
Spring3D(GLfloat xpos, GLfloat ypos, GLfloat zpos) {
pos = glm::vec3(xpos, ypos, zpos);
}
void update(glm::vec3 target);
};
JellyfishInstance
struct JellyfishInstance {
glm::vec3 pos;
GLfloat scale; // 相对父关节的缩放
GLfloat time;
std::map<int, Spring3D*> sx;
JellyfishInstance(glm::vec3 pos, GLfloat scale, GLfloat time) {
this->pos = pos;
this->scale = scale;
this->time = time;
for (int j = 0; j < JOINT_COUNT; j++) {
this->sx[j] = new Spring3D(pos[0], pos[1] - 1 - 1 * j * this->scale, pos[2]);
}
}
void draw();
void simulate();
};
蒙皮动画
guillaumeblanc / ozz-animation
局部姿势是关节相对于父关节来指定的,是一种常见的姿势。局部姿势存储为 $TQS$ 的格式, 表示相对与父关节的位置、朝向、缩放,根关节的父节点可以认为是世界坐标系原点。
关节在三维软件里通常是显示成一个点或者一个球,实际上,每个关节定义了一个坐标空间。 在数学上,关节姿势就是一个仿射变换,用 $P_j$ 表示关节 $j$ 代表的仿射变换, 它是一个 $4\times 4$ 的矩阵,它由平移向量 $T_j$,旋转矩阵 $R_j$ 以及对角缩放矩阵 $S_j$ 组成。
\[P_j=\left[\begin{matrix} R_jS_j & T_j \\ 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right]\]局部关节姿势可以表示为:
struct JointPose
{
Quaternion m_rot; // 相对父关节朝向
Vector3 m_trans; // 在父关节中的坐标
Vector3 m_scale; // 相对父关节的缩放
};
局部关节姿势矩阵 $P_j$ 作用到以关节 $j$ 坐标系表示的点或者向量时,其结果是将点或者向量变换到父关节坐标空间表示的点。
这样关节 8 的 蒙皮矩阵 就是 \(F_8=G_8O_8=P_1'P_7'P_8'(P_1P_7P_8)^{-1}\)
加权平均的计算时,顶点绑定的所有骨架的权重和为 1。通常设每个顶点最多绑定到 4 个骨架,程序存储如下:
struct SkinnedVertex
{
float m_position[3]; // 顶点位置(x, y, z)
float m_normal[3]; // 顶点法向量(Nx, Ny, Nz)
float m_u, m_v; // 纹理坐标
U8 m_jointIndex[4]; // 关节的索引
float m_jointWeight[4]; // 关节权重
};
上面提到过 蒙皮矩阵 ,但是还没正式定义,蒙皮矩阵就是把顶点从 绑定姿势 变换到骨骼的 当前姿势 的矩阵。 蒙皮矩阵和前面的 基变更 矩阵不同,它只是把顶点变换到新的位置,顶点变换前后都在世界空间中(或模型空间中)。 和上面一样用 $F_j$ 表示关节 $j$ 的蒙皮矩阵,假设某个顶点 $v$ 受到上面关节 14、18、15、25 的影响, 对应点权重分别为 $w_1,w_2,w_3,w_4$,则顶点 $v$ 的最终变换位置为: \(v'=w_1F_{14}v+w_2F_{18}v+w_3F_{15}v+w_4F_{25}v\) 上面公式就是顶点的蒙皮计算方法。
绘制主流程
void drawScene(float aspect) {
// interact();
// requestAnimFrame(animate);
refreshCurrentTimeAndTexture();
refreshMatrix(aspect);
interpolateTargets(); // 内插 Target
simulateTargets();
interpolateJellyfish();
drawJellyfish();
}
矩阵更新
void refreshMatrix(float aspect) {
M4x4_makePerspective(g_localParam.camera.fov, aspect,
g_localParam.camera.znear, g_localParam.camera.zfar,
g_programData.mProjection);
M4x4_makeTranslate3(0, 0, 0, g_programData.mWorld);
M4x4_makeTranslate3(0, 0, 0, g_programData.mView);
M4x4_translate3(g_localParam.camera.translate[0], 0, 0, g_programData.mView, g_programData.mView);
M4x4_translate3(0, -g_localParam.camera.translate[1], 0, g_programData.mView, g_programData.mView);
M4x4_translate3(0, 0, g_localParam.camera.translate[2], g_programData.mView, g_programData.mView);
M4x4_rotate(g_localParam.camera.rotate[0], glm::vec3(1, 0, 0), g_programData.mView, g_programData.mView);
M4x4_rotate(g_localParam.camera.rotate[1], glm::vec3(0, 1, 0), g_programData.mView, g_programData.mView);
// Set necessary matrices
M4x4_mul(g_programData.mView, g_programData.mWorld, g_programData.mWorldView);
M4x4_mul(g_programData.mProjection, g_programData.mWorldView, g_programData.mWorldViewProj);
M4x4_inverseOrthonormal(g_programData.mView, g_programData.mViewInv);
g_localParam.camera.eye = glm::vec3(-g_programData.mViewInv[12], -g_programData.mViewInv[13], -g_programData.mViewInv[14]);
}
Target 动画模拟
void simulateTargets() {
for (int i = 0; i < g_jellyfishTargets.count; i++) {
// SET TIME
float xtime = g_userParam.userSpeed * 16 / (g_jellyfishTargets[i]->scale + 1);
g_jellyfishTargets[i]->time += xtime * g_jellyfishTargets[i]->speed;
// MOVE
time_t ztime = time(NULL) * 1000;
float speed = g_jellyfishTargets[i]->scale * g_userParam.userSpeed * 2.8;
float x = g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos[2] + g_jellyfishTargets[i]->id + ztime / 10000;
float y = g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos[0] + g_jellyfishTargets[i]->id + ztime / 10000;
float z = g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos[1] + g_jellyfishTargets[i]->id + ztime / 10000;
glm::vec3 flow = glm::vec3(
speed * sin(x * g_userParam.userTurbulence),
speed * sin(y * g_userParam.userTurbulence),
speed * sin(z * g_userParam.userTurbulence)
);
V3_add(g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos, flow, g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos);
// REPEL
// 鱼和鱼之间的缠绕
for (int j = 0; j < g_jellyfishTargets.count; j++) {
if (i != j) {
glm::vec3 delta = V3_sub(g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos, g_jellyfishTargets[j]->pos);
float dist = V3_length(delta);
glm::vec3 dir = V3_normalize(delta);
glm::vec3 force = V3_scale(dir, pow(1.0 / dist, 3) * 20000);
V3_add(g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos, force, g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos);
}
}
// CENTER
g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos[0] *= 0.995;
g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos[1] *= 0.995;
g_jellyfishTargets[i]->pos[2] *= 0.995;
}
}
单个水母关节动画
void Spring3D::update(glm::vec3 target) {
glm::vec3 delta = V3_sub(target, this->pos);
glm::vec3 deltaNorm = V3_normalize(delta);
deltaNorm = V3_scale(deltaNorm, this->spring); // 弹性
delta = V3_sub(delta, deltaNorm);
GLfloat stiffness = 0.2; // 刚度
GLfloat mass = 0.1; // 质量
GLfloat damping = 0.1; // 阻尼
glm::vec3 force = V3_scale(delta, stiffness); // 刚度
force[1] += this->gravity; // 向下的重力
glm::vec3 accel = V3_scale(force, 1 / mass); // 加速度
glm::vec3 veloc = glm::vec3(0, 0, 0); // 速度速率
V3_add(force, accel, veloc);
veloc = V3_scale(veloc, damping); // 阻尼
V3_add(this->pos, veloc, this->pos);
M4x4_makeLookAt(this->pos, target, g_localParam.camera.eye, this->lookat);
}
void JellyfishInstance::simulate() {
GLfloat propel = 1; // 推力
propel = (sin(this->time + PI) + 0.6) * 0.2; // 推搡
for (int j = 0; j < JOINT_COUNT; j++) {
if (j == 0) {
this->sx[0]->spring = 1.295 * this->scale * (2.0 - propel); // 弹性
this->sx[0]->update(this->pos);
this->sx[0]->gravity = -0.01; // 向下的重力
}
else {
this->sx[j]->spring = 2.95 * this->scale; // 弹性
this->sx[j]->update(this->sx[j - 1]->pos);
this->sx[j]->gravity = -0.02; // 向下的重力
}
M4x4_makeTranslate(this->sx[j]->pos, g_programData.joint[j]);
M4x4_mul(g_programData.joint[j], this->sx[j]->lookat, g_programData.joint[j]);
M4x4_scale1(this->scale, g_programData.joint[j], g_programData.joint[j]);
M4x4_translate3(0, j * 3, 0, g_programData.joint[j], g_programData.joint[j]);
}
}
绘制部分
int sort3d(glm::vec4& a, glm::vec4& b) {
glm::vec3 va(a[1], a[2], a[3]);
glm::vec3 vb(b[1], b[2], b[3]);
glm::vec3 eye = glm::vec3(
-g_localParam.camera.eye[0],
-g_localParam.camera.eye[1] + 20,
-g_localParam.camera.eye[2]);
GLfloat lenva = V3_length(V3_sub(eye, va));
GLfloat lenvb = V3_length(V3_sub(eye, vb));
if (lenva > lenvb) {
return -1;
}
if (lenva < lenvb) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int cmpfunc(const void* a, const void* b) {
return sort3d(*(glm::vec4*)a, *(glm::vec4*)b);
}
void drawJellyfish() {
qsort(&g_jellyfish.order[0], g_jellyfish.order.size(), sizeof(glm::vec4), cmpfunc);
for (int i = 0; i < g_jellyfish.count; i++) {
int index = g_jellyfish.order[i][0];
if (g_jellyfish[index]) {
g_jellyfish[index]->simulate();
g_jellyfish[index]->draw();
}
}
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
project(jellyfish)
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS_DEBUG "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS_DEBUG} -D_DEBUG")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG} -D_DEBUG")
add_definitions(-DUNICODE -D_UNICODE)
set(OGL3RD_DIR "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/../../opengl-3rd")
# json botan lz4
# add_subdirectory(${OGL3RD_DIR}/thirdparty thirdparty.build)
include_directories(
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glad/include
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glfw-3.3.2.bin.WIN32/glfw-3.3.2.bin.WIN32/include
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glew-2.2.0-win32/glew-2.2.0/include
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glm-0.9.9.8/glm
${OGL3RD_DIR}/stb
${OGL3RD_DIR}/thirdparty/json-3.9.1/single_include
)
link_directories(
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glew-2.2.0-win32/glew-2.2.0/lib/Release/Win32
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glfw-3.3.2.bin.WIN32/glfw-3.3.2.bin.WIN32/lib-vc2017
${OGL3RD_DIR}/glad/lib/vs2017_win32/Release
)
FILE(GLOB_RECURSE OGL_HEADERS
RELATIVE "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}"
"${OGL3RD_DIR}/learnopengl/*.*"
)
source_group(TREE "${OGL3RD_DIR}" FILES ${OGL_HEADERS})
add_executable(
jellyfish
jellyfish.h
jellyfish.cpp
jellyfishImpl.cpp
jellyfishMath.cpp
jellyfishUtil.cpp
jellyfishVertex.cpp
jellyfishTexture.cpp
jellyfishShader.cpp
jellyfishSimulator.cpp
jellyfish.vert
jellyfish.frag
${OGL3RD_DIR}/stb/stb_image.cpp
${OGL_HEADERS}
)
target_link_libraries(
jellyfish
glfw3 glew32s
opengl32 # fakedriver
glad
)
set_target_properties(jellyfish PROPERTIES RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY_DEBUG "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/product")
set_target_properties(jellyfish PROPERTIES VS_DEBUGGER_WORKING_DIRECTORY "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/product")
Shader
jellyfish.vert
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aVertexPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aVertexNormal;
layout (location = 2) in vec3 aVertexColor;
layout (location = 3) in vec3 aTextureCoord;
layout (location = 4) in vec4 aSkinWeight;
uniform mat4 uWorld;
uniform mat4 uViewInv;
uniform mat4 uWorldView;
uniform mat4 uWorldViewProj;
uniform mat4 uJoint0;
uniform mat4 uJoint1;
uniform mat4 uJoint2;
uniform mat4 uJoint3;
uniform mat4 uJoint0InvTranspose;
uniform float uCurrentJellyfishTime;
out vec4 vWorld;
out vec3 vTextureCoord;
out vec3 vDiffuse;
out vec3 vFresnel;
void main() {
// 顶点动画
float dpi = 6.2831853;
float pi = 3.14159265;
float hpi = 1.570796325;
float time = mod(uCurrentJellyfishTime+aVertexPosition.y, dpi);
float offset = smoothstep(0.0,1.,max(0.,-aVertexPosition.y-0.8)/10.);
vec3 anim = (vec3(aVertexColor.x,aVertexColor.y,aVertexColor.z)/8.0*sin(time) * (1.-offset));
vec3 pos = aVertexPosition + anim;
// 骨骼蒙皮动画算法(Linear Blending Skinning)
pos = vec3(uJoint0 * vec4(pos, 1.0))*aSkinWeight.x +
vec3(uJoint1 * vec4(pos, 1.0))*aSkinWeight.y +
vec3(uJoint2 * vec4(pos, 1.0))*aSkinWeight.z +
vec3(uJoint3 * vec4(pos, 1.0))*aSkinWeight.w;
vec3 nrm = vec3(uJoint0InvTranspose * vec4(aVertexNormal, 1.0));
// 矩阵
vWorld = uWorld * vec4(pos, 1.0);
vec4 WorldViewProj = uWorldViewProj * vec4(pos, 1.0);
// vertex normal
vec3 VertexNormal = normalize(nrm);
// vertex eye vector
vec3 WorldEyeVec = normalize(vWorld.xyz - uViewInv[3].xyz);
// diffuse
vec3 lightDir = vec3(0.0,1.0,0.0);
vec3 lightCol = vec3(0.6,0.4,0.1);
vec3 ambientCol = vec3(0.5,0.2,0.1);
float diffuseProduct = max(dot(normalize(VertexNormal.xyz), lightDir), 0.0);
vDiffuse = lightCol * vec3(diffuseProduct) + ambientCol;
// 菲涅尔反射 (Fresnel Reflection)
vec3 fresnelColor = vec3(0.2,0.5,0.6);
float fresnelProduct = pow(1.0-max(abs(dot(VertexNormal, -WorldEyeVec)), 0.0), 2.0);
vFresnel = fresnelColor * vec3(fresnelProduct);
// texture coords
vTextureCoord = aTextureCoord;
gl_Position = WorldViewProj;
}
jellyfish.frag
#version 330 core
uniform sampler2D uSampler0;
uniform sampler2D uSampler1;
uniform sampler2D uSampler2;
uniform float uCurrentTime;
in vec4 vWorld;
in vec3 vTextureCoord;
in vec3 vDiffuse; // 漫射的
in vec3 vFresnel; // Fresnel 效果
out vec4 FragColor;
void main() {
vec3 caustics = texture(uSampler1, vec2((vWorld.x)/48.+uCurrentTime/12., (vWorld.z-vWorld.y)/95.)).rgb; // 水波纹
vec4 colorMap = texture(uSampler0, vec2(vTextureCoord.s, vTextureCoord.t));
FragColor = vec4(((vDiffuse + caustics)*colorMap.rgb) + vFresnel, colorMap.a);
}
参考资料快照
- https://blog.csdn.net/douzhq/article/details/116998068
- https://www.cnblogs.com/tandier/p/10087656.html
- https://www.qiujiawei.com/linear-algebra-19/
- https://github.com/arodic/WebGL-Fluid-Simulation
- https://github.com/arodic/Chrysaora
- https://github.com/arodic/jellyfish
- https://github.com/guillaumeblanc/ozz-animation
 .
.