图形学笔记 -- 用 Bullet Physics 和 OpenGL 实现的 抛箱子
A simple box shooter using Bullet Physics and OpenGL. 物理碰撞。用 Bullet Physics 和 OpenGL 实现的 抛箱子。有机会实现一个桌面壁纸泡泡,泡泡之间可以撞来撞去。 甚至粒子系统可以直接加入碰撞检测。
Bullet Physics 是一个开源的物理模拟引擎,世界三大物理引擎之一(另外两种是 Havok 和 PhysX)。 Bullet 是一个跨平台的开源物理引擎,支持三维碰撞检测、柔体动力学和刚体动力学,多用于游戏开发和电影制作中。Bullet 物理库在 zlib 协议下发布。 Right-handed coordinate system in bullet,和 OpenGL 一致。一个人写的,歪果人就是牛。 Bullet 的主要作者为 Erwin Coumans,曾经就职于索尼电脑娱乐美国研发职务 2003 到 2010 年,就职于 AMD 公司到 2014 年,现就职于 Google 公司。
Box Shooter
A simple game that one can throw box to a pile of boxes to drop some of them. The implementation is using using OpenGL and Bullet Physics.
源码位置:https://github.com/hawkhai/box_shooter.git 实验效果:
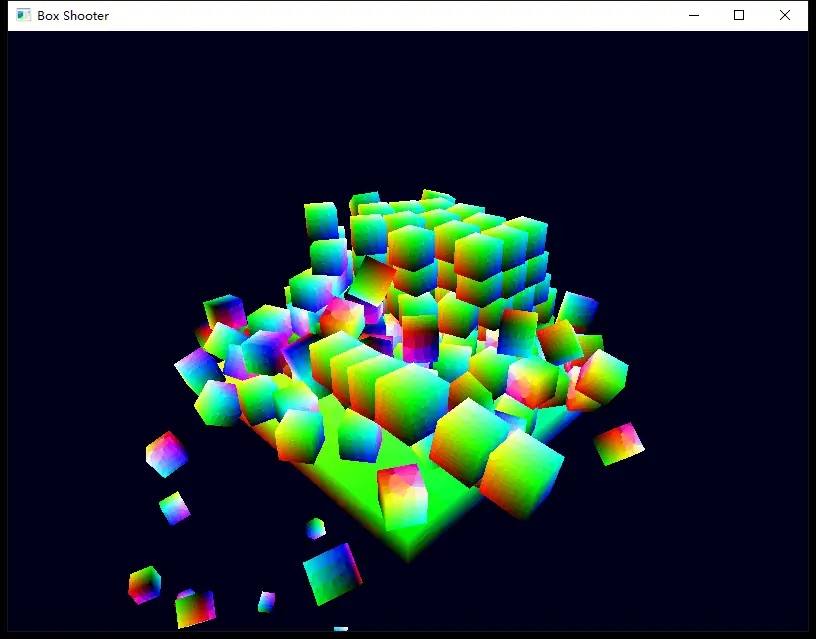
Installing Box Shooter
To install Box Shooter, follow these steps:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. # Using CMake
make # make all
BulletPhysics 基本概念
创建并初始化物理世界
// 设置世界的空间大小,限定刚体运动的空间范围
btVector3 worldAabbMin(-10000, -10000, -10000);
btVector3 worldAabbMax(10000, 10000, 10000);
// 设置最大刚体数
int maxProxies = 1024;
// 利用以上配置创建粗测阶段所需参数
btAxisSweep3* broadphase = new btAxisSweep3(worldAabbMin, worldAabbMax, maxProxies);
// 创建好碰撞配置
// 例如一些多人射击游戏中,队友之间不会发生碰撞,但是和其他物体都能发生碰撞
btDefaultCollisionConfiguration* collisionConfiguration = new btDefaultCollisionConfiguration();
btCollisionDispatcher* dispatcher = new btCollisionDispatcher(collisionConfiguration);
// 创建求解器
btSequentialImpulseConstraintSolver* solver = new btSequentialImpulseConstraintSolver();
// 使用以上创建的设置来创建物理世界
btDiscreteDynamicsWorld* dynamicsWorld = new btDiscreteDynamicsWorld(dispatcher, broadphase, solver, collisionConfiguration);
// 设置物理世界重力(这里在 y 轴上的重力设为 10N/kg)
dynamicsWorld->setGravity(btVector3(0, -10, 0));
释放代码:
#define SAFE_DELETE_PTR(ptr) do{ if (ptr) {delete ptr;ptr = nullptr;}} while (0);
PhysicsWorld::~PhysicsWorld() {
// 必须先 delete DynamicWorld
SAFE_DELETE_PTR(mDynamicsWorld);
// 再 delete 其他相关资源
SAFE_DELETE_PTR(mBroadphase);
SAFE_DELETE_PTR(mCollisionConfiguration);
SAFE_DELETE_PTR(mDispatcher);
SAFE_DELETE_PTR(mSolver);
}
刚体
包含形状,摩擦系数,阻尼系数,弹性系数等属性。
地面一般是固定不变的,所以它是静态刚体,我们设置 mass 时要设置为 0。地面是平面形状的,所以形状要设置成 btStaticPlaneShape(即静态平面形状)。 (密度为 0 时会被 Bullet 认为是静态刚体,非 0 时则认为是动态刚体)
创建一个平面状的静态刚体(作为地面)的代码:
// 创建 物体的初始位置旋转角度信息:旋转角度 0,位置在 Y 轴 -1 距离
btDefaultMotionState* groundMotionState = new btDefaultMotionState(btTransform(btQuaternion(0, 0, 0, 1), btVector3(0, -1, 0)));
// 创建 静态平面形状
btCollisionShape* groundShape = new btStaticPlaneShape(btVector3(0, 1, 0), 1);
// 生成设置信息
btRigidBody::btRigidBodyConstructionInfo groundRigidBodyCI(0, groundMotionState, groundShape, btVector3(0, 0, 0));
// 根据设置信息 创建刚体
btRigidBody* groundbody = new btRigidBody(groundRigidBodyCI);
// 设置摩擦系数 0.5
groundbody->setFriction(0.5f);
// 将地面刚体添加到 物理世界
dynamicWorld->addRigidBody(groundbody);
创建一个球状的动态刚体的代码:
// 创建 物体的初始位置旋转角度信息:旋转角度 0,位置在 Y 轴 10 距离的高空
btDefaultMotionState* ballMotionState = new btDefaultMotionState(btTransform(btQuaternion(0, 0, 0, 1), btVector3(0, 10, 0)));
// 创建 半径 0.5 的球体形状
btCollisionShape* ballShape = new btSphereShape(0.5);
// 设置密度(特殊地,密度为 0 时会被认为静态刚体,非 0 时则作为动态刚体)
int mass = 10;
// 惯性
btVector3 inertia;
// 根据密度自动计算并设置惯性
ballShape->calculateLocalInertia(mass, inertia);
// 生成设置信息
btRigidBody::btRigidBodyConstructionInfo groundRigidBodyCI(mass, ballMotionState, ballShape, inertia);
// 根据设置信息 创建刚体
btRigidBody* ballBody = new btRigidBody(groundRigidBodyCI);
// 设置摩擦系数 0.5
ballBody->setFriction(0.5f);
// 将该刚体添加到物理世界里
dynamicsWorld->addRigidBody(ballBody);
开始模拟
物理引擎的位置角度信息和渲染逻辑的位置角度信息是分别独立的,物理模拟后须将物理引擎的位置角度信息赋给渲染逻辑的位置角度信息。
void updateScene(float deltaTime) {
// 主循环函数的其它内容(一般是逻辑处理)
// balabala.....
// 物理世界模拟
// 通过 10 次子步骤求解,模拟出 deltaTime 后的物理世界变化。
dynamicsWorld->stepSimulation(deltaTime, 10);
// 更新物理世界每一个物体
auto & objectArray = dynamicsWorld->getCollisionObjectArray();
for (int i = 0; i < objectArray.size(); ++i)
{
// 处于不活动状态或者是静态刚体的话,则不处理
if (!objectArray[i]->isActive() || objectArray[i]->isStaticObject()) continue;
Transform* object = reinterpret_cast<Transform*>(objectArray[i]->getUserPointer());
// 没有用户指针的话,则不处理
if (!object)continue;
// 更新目标物体的位置
const auto & pos = objectArray[i]->getWorldTransform().getOrigin();
object->setPosition(pos.x(), pos.y(), pos.z());
// 更新目标物体的旋转角度
const auto & rotationM = objectArray[i]->getWorldTransform().getRotation();
object->setRotation(rotationM.getX(), rotationM.getY(), rotationM.getZ(), rotationM.getW());
}
// 主循环函数的其他内容(一般是渲染)
// bala......
}
删除刚体
for (int i = 0; i < objectArray.size(); ++i)
{
// 清除待删除物理刚体
int entityState = reinterpret_cast<int>(objectArray[i]->getUserPointer());
// 本文将待删除物理刚体的用户指针指向 Entity::NoEntity(-1 值)作为待删除标记,也可用其它来作为标记
if (entityState == Entity::NoEntity) {
m_dynamicsWorld->removeCollisionObject(objectArray[i]);
--i; // 删除后要退回一位
continue;
}
... // 其它代码
}
相机控制
右手坐标系。移除 roll。Z 轴正方向为前进方向。
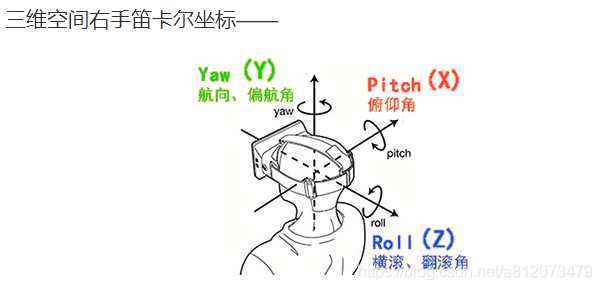

pitch():俯仰,将物体绕 X 轴旋转(localRotationX)
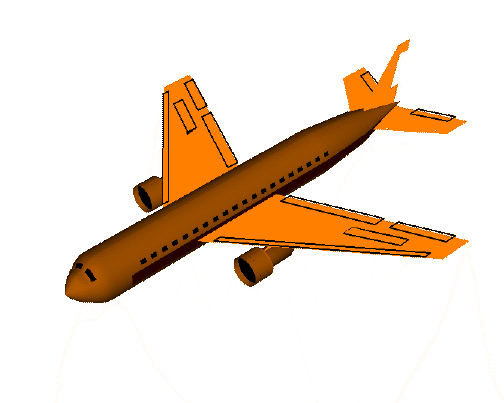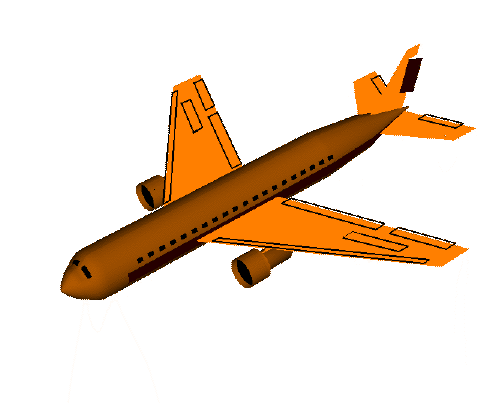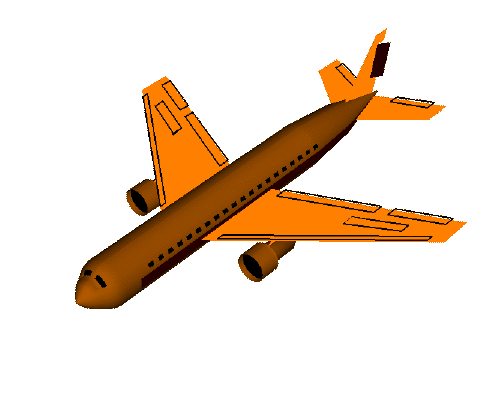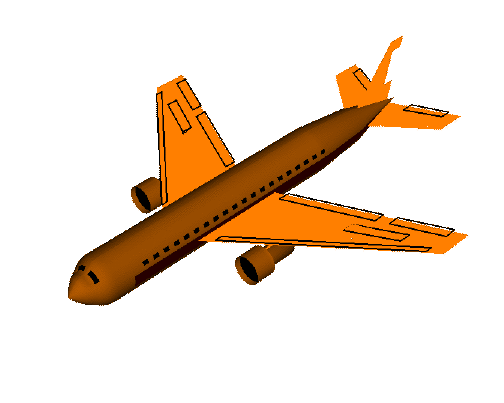
yaw():航向,将物体绕 Y 轴旋转(localRotationY)
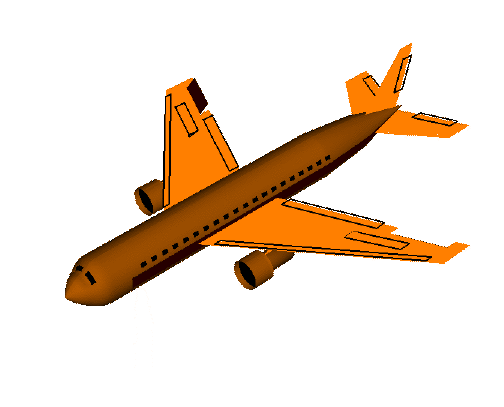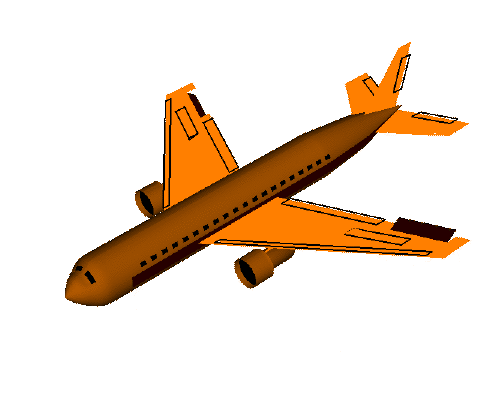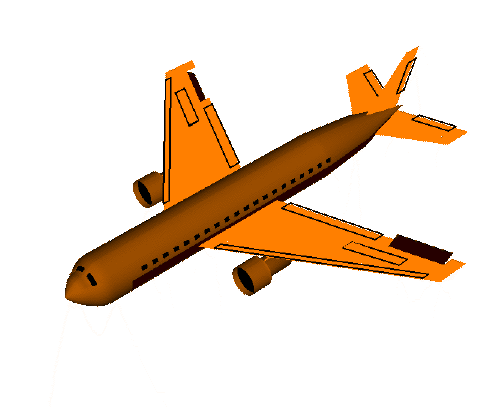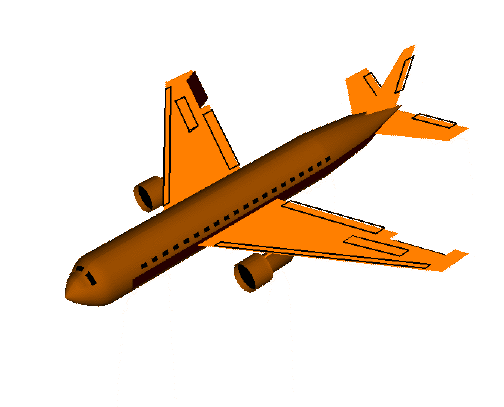
roll():横滚,将物体绕 Z 轴旋转(localRotationZ)
void Camera::update()
{
front.x = cos(glm::radians(yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(pitch));
front.z = cos(glm::radians(pitch)) * sin(glm::radians(yaw));
front = glm::normalize(front);
right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(front, worldUp));
up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(right, front));
}
glm::mat4 Camera::calculateViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(position, position + front, up);
}
// GLFW_KEY_W
// GLFW_KEY_S
// GLFW_KEY_A
// GLFW_KEY_D
空间位置
创建箱子
static GLfloat vertices[] = {
// front
-1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
// back
-1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, 1.0, -1.0 };
箱子边长为 2。
创建场景
Box *ground = new Box(2, -2, 2);
ground->scaleBox(glm::vec3(10.0f, 1.0f, 10.0f));
地板放在 (2, -2, 2),然后变大的地板为:20 x 2 x 20。
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
{
shapes.push_back(new Box(i, j, k));
}
}
}
125 个箱子,放在了 [[0,4], [0,4], [0,4]] 位置。程序启动可以发现,箱子由于挤压,存在一个变大和下落的过程。
相机位置为 (-20.0f, 20.0f, -20.0f),左右摇头 45 度,上下点头 30 度:
camera = new Camera(
glm::vec3(-20.0f, 20.0f, -20.0f), // glm::vec3 Position
glm::vec3(.0f, 1.0f, .0f), // glm::vec3 Up
45.0f, // GLfloat Yaw 左右摇头 45 度。
-30.0f, // GLfloat Pitch 上下点头,30 度。
5.0f); // GLfloat Movespeed
抛箱子
从相机位置抛箱子 new Box(-20.0f, 20.0f, -20.0f) 。
从相机的角度抛出去。
auto camera_dir = camera->get_front();
direction.setX(camera_dir.x);
direction.setY(camera_dir.y);
direction.setZ(camera_dir.z);
body->setLinearVelocity(direction * 25); // 初始线速度
源码解析
初始化 物理空间 init_physics
void init_physics()
{
collisionConfiguration = new btDefaultCollisionConfiguration();
dispatcher = new btCollisionDispatcher(collisionConfiguration);
overlappingPairCache = new btDbvtBroadphase();
solver = new btSequentialImpulseConstraintSolver;
dynamicsWorld = new btDiscreteDynamicsWorld(dispatcher, overlappingPairCache, solver,
collisionConfiguration);
}
创建视觉 箱子 init_visual_shapes
void init_visual_shapes()
{
// Items
// Ground
Box *ground = new Box(2, -2, 2);
ground->scaleBox(glm::vec3(10.0f, 1.0f, 10.0f));
shapes.push_back(ground);
// Other
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
{
shapes.push_back(new Box(i, j, k));
}
}
}
}
创建物理 箱子 init_collision_shapes
void init_collision_shapes()
{
// create a few basic rigid bodies
{
btCollisionShape *groundShape = new btBoxShape(btVector3(btScalar(10.), btScalar(1.), btScalar(10.)));
collisionShapes.push_back(groundShape);
btTransform groundTransform;
groundTransform.setIdentity();
auto origin = shapes[0]->getOrigin();
groundTransform.setOrigin(btVector3(origin.x, origin.y, origin.z));
btScalar mass(0.);
// rigidboy is dynamic if and only if mass is non zero, otherwise static
bool isDynamic = (mass != 0.f);
btVector3 localInertia(0, 0, 0);
if (isDynamic)
groundShape->calculateLocalInertia(mass, localInertia);
// using motionstate is optional, is provides interpolation capabilities, and only synchronizes 'active' objects
btDefaultMotionState *myMotionState = new btDefaultMotionState(groundTransform);
btRigidBody rbInfo(mass, myMotionState, groundShape, localInertia);
btRigidBody *body = new btRigidBody(rbInfo);
// add the body to the dynamics world
dynamicsWorld->addRigidBody(body);
}
// create a dynamic rididbody
{
for (auto shape : shapes)
{
if (shape->getOrigin().y < 0) // Skip the round.
continue;
auto origin = shape->getOrigin();
btCollisionShape *colShape = new btBoxShape(btVector3(1, 1, 1));
collisionShapes.push_back(colShape);
// Create Dynamic Objects
btTransform startTransform;
startTransform.setIdentity();
btScalar mass(1.f);
// rigidbody is dynamic if and only if mass is non zero, otherwise static
bool isDynamic = (mass != 0.0f);
btVector3 localInertia(0, 0, 0);
if (isDynamic)
colShape->calculateLocalInertia(mass, localInertia);
startTransform.setOrigin(btVector3(origin.x, origin.y, origin.z));
// using motionstate is recommended, is provides interpolation capabilities, and only synchronizes 'active' objects
btDefaultMotionState *myMontionState = new btDefaultMotionState(startTransform);
btRigidBody::btRigidBodyConstructionInfo rbInfo(mass, myMontionState, colShape, localInertia);
btRigidBody *body = new btRigidBody(rbInfo);
dynamicsWorld->addRigidBody(body);
}
}
}
检查物理变化 check_collisions
步进一下,然后取每个箱子状态,该移除的就移除。
void check_collisions()
{
dynamicsWorld->stepSimulation(deltaTime, 10); // 步进一下
// print positions of all objects
for (int j = dynamicsWorld->getNumCollisionObjects() - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
btCollisionObject *obj = dynamicsWorld->getCollisionObjectArray()[j];
btRigidBody *body = btRigidBody::upcast(obj);
btTransform trans;
if (body && body->getMotionState())
{
body->getMotionState()->getWorldTransform(trans);
}
else
{
trans = obj->getWorldTransform();
}
trans.getOpenGLMatrix(glm::value_ptr(shapes.at(j)->set_transformation()));
if (float(trans.getOrigin().getY() > -100.0))
continue;
// Delete form bullet
if (body && body->getMotionState())
{
delete body->getMotionState();
}
dynamicsWorld->removeCollisionObject(obj);
delete obj;
btCollisionShape *shape = collisionShapes[j];
collisionShapes[j] = 0;
shapes.erase(std::begin(shapes) + j);
}
}
鼠标点击发射 箱子 process_keys
void process_keys()
{
int posx, posy;
bool mouse_clicked;
std::tie(posx, posy, mouse_clicked) = mainwindow->mouse_feedback();
if (mouse_clicked)
{
shapes.push_back(new Box(-20.0f, 20.0f, -20.0f));
auto origin = shapes.back()->getOrigin();
btCollisionShape *colShape = new btBoxShape(btVector3(1, 1, 1));
collisionShapes.push_back(colShape);
// Create Dynamic Objects
btTransform startTransform;
startTransform.setIdentity();
btScalar mass(1.f);
// rigidbody is dynamic if and only if mass is no zero, otherwise static
bool isDynamic = (mass != 0.f);
btVector3 localInertia(0, 0, 0);
if (isDynamic)
colShape->calculateLocalInertia(mass, localInertia);
startTransform.setOrigin(btVector3(origin.x, origin.y, origin.z));
// using motionstate is recommended, it provides interpolation capabilities, and only synchronizes 'active' objects
btDefaultMotionState *myMontionState = new btDefaultMotionState(startTransform);
btRigidBody::btRigidBodyConstructionInfo rbInfo(mass, myMontionState, colShape, localInertia);
btRigidBody *body = new btRigidBody(rbInfo);
btVector3 direction;
auto camera_dir = camera->get_front();
direction.setX(camera_dir.x);
direction.setY(camera_dir.y);
direction.setZ(camera_dir.z);
body->setLinearVelocity(direction * 25);
dynamicsWorld->addRigidBody(body);
}
}
清理 物理空间 delete_physics
void delete_physics()
{
// delete dynamics world
delete dynamicsWorld;
// delete solver
delete solver;
// delete broadphase
delete overlappingPairCache;
// delete dispatcher
delete dispatcher;
delete collisionConfiguration;
// next line is optionl: it will be cleared by the destructor when the array goes out of scope
collisionShapes.clear();
}
CMakeLists.txt
这两个工程配置也非常简洁。
external
add_definitions(
-DTW_STATIC
-DTW_NO_LIB_PRAGMA
-DTW_NO_DIRECT3D
-DGLEW_STATIC
-D_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
)
### GLFW ###
add_subdirectory (glfw-3.1.2)
include_directories(
glfw-3.1.2/include/GLFW/
glew-1.13.0/include/
)
set(OPENGL_LIBRARY
${OPENGL_LIBRARY}
-lGL -lGLU -lXrandr -lXext -lX11 -lrt
${CMAKE_DL_LIBS}
${GLFW_LIBRARIES}
)
### GLEW ###
set(GLEW_SOURCE
glew-1.13.0/src/glew.c
)
set(GLEW_HEADERS
)
add_library( GLEW_1130 STATIC
${GLEW_SOURCE}
${GLEW_INCLUDE}
)
target_link_libraries(GLEW_1130
${OPENGL_LIBRARY}
${EXTRA_LIBS}
)
### BULLET ###
# Bullet already has a CMakeLists.txt so let's use these
set(BULLET_VERSION 2.81)
include_directories(
bullet-2.81-rev2613/src
)
add_subdirectory( bullet-2.81-rev2613/src/BulletSoftBody )
add_subdirectory( bullet-2.81-rev2613/src/BulletCollision )
add_subdirectory( bullet-2.81-rev2613/src/BulletDynamics )
add_subdirectory( bullet-2.81-rev2613/src/LinearMath )
box_shooter
# CMake entry point
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.0)
project (Box_Shooter)
find_package(OpenGL REQUIRED)
# Compile external dependencies
add_subdirectory (external)
include_directories(
external/glfw-3.1.2/include/
external/glm-0.9.7.1/
external/glew-1.13.0/include/
external/bullet-2.81-rev2613/src/
)
set(ALL_LIBS
${OPENGL_LIBRARY}
glfw
GLEW_1130
)
add_definitions(
-DTW_STATIC
-DTW_NO_LIB_PRAGMA
-DTW_NO_DIRECT3D
-DGLEW_STATIC
-D_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
)
LINK_LIBRARIES(
BulletDynamics BulletCollision LinearMath
)
add_executable(box_shooter
src/box_shooter.cpp
src/Mesh.cpp
src/Shader.cpp
src/Window.cpp
src/Camera.cpp
)
target_link_libraries(box_shooter
${ALL_LIBS}
)
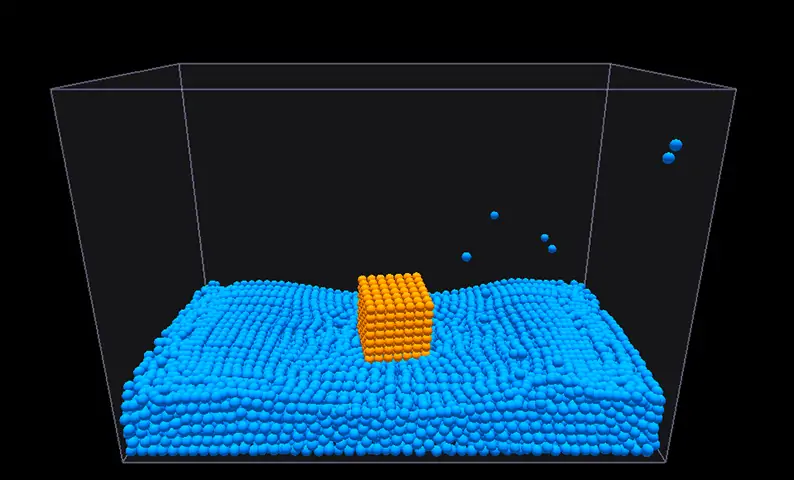
流固耦合模拟
流体与刚体交互模拟。流体采用 SPH 算法,刚体使用 Bullet 计算。 刚体由粒子组成,使用 btCompoundShape 实现,用于计算流体对刚体的作用力。
Refs
- [1] C++ 3D 物理引擎库 BulletPhysics 基本使用
- [2] 【Bullet 引擎】复杂碰撞体 —— btCompoundShape

- [3] 【Bullet 引擎】复杂碰撞体 —— btCompoundShape
参考资料快照
 .
.